54 Małgorzata Wójtowicz
Streszczenie
Zanim chorzy psychicznie jako „niegodni życia” zginęli w czasie II wojny światowej w narodowosocjalistycznej „Akcji T4”, niemiecka psychiatria
sły nęła nie tylko ze światowej rangi uczonych, ale też ze wspaniałych zakładów psychiatrycznych. Były one profesjonalnie zorganizowane wed -
ług najnowszych osiągnięć w tej dziedzinie medycyny i – w swojej szczytowej fazie – niezwykle malowniczo zaaranżowane pod względem
urbanistycznym. Niektóre z nich nasuwają skojarzenia z Howardowskim ruchem „miast ogrodów”, w Niemczech realizowanym w praktyce po
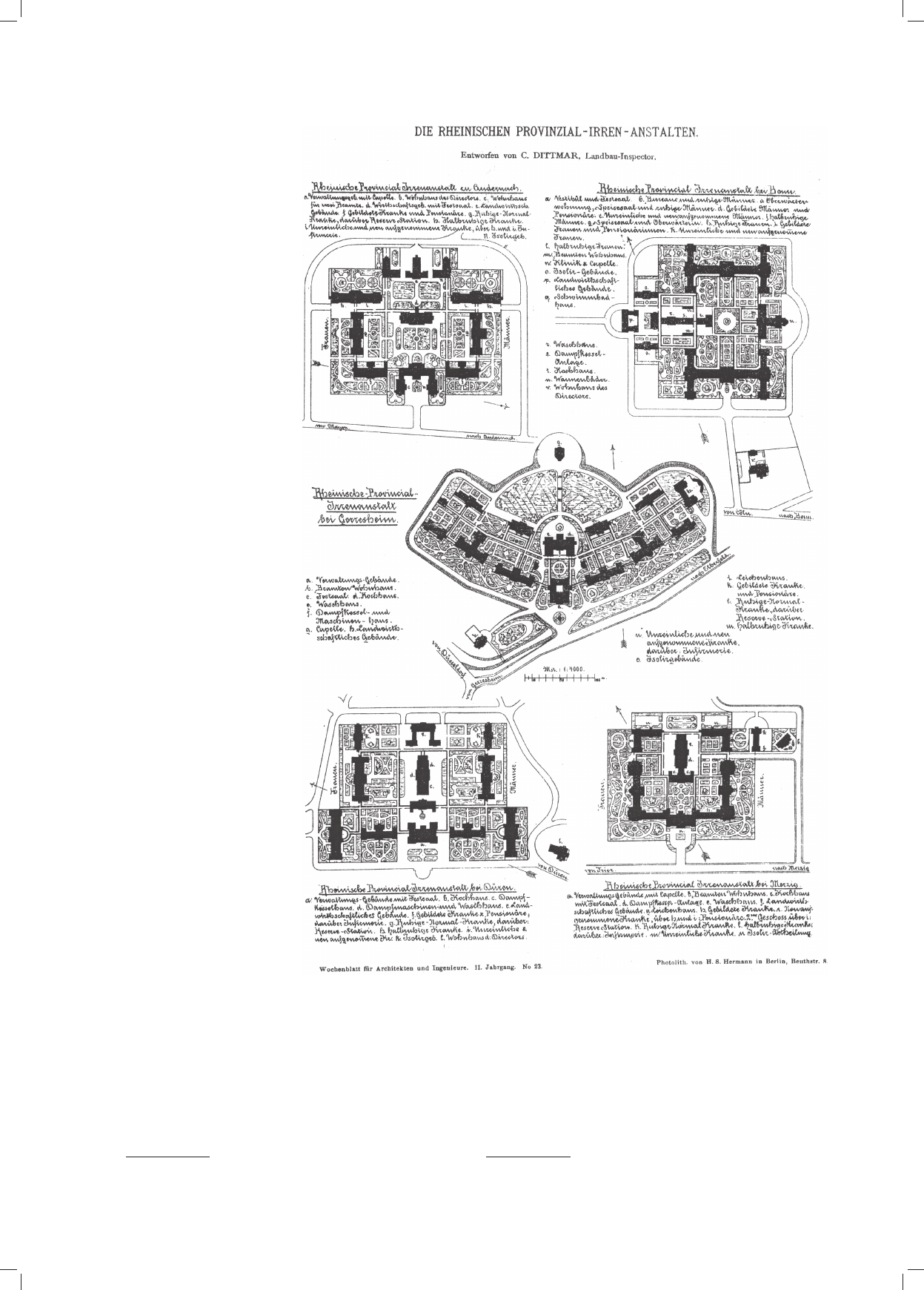
utworzeniu w 1902 r. „Deutsche Gartenstadtgesellschaft”. Bezpośrednio można je wywieść ze szpitali pawilonowych, ale nie ulega wątpliwości,
że tworzyły samowystarczalne osady z przemyślanymi założeniami parkowymi. Właśnie w takich zakładach (które po wojnie wznowiły swoją
działalność) niezamożnym pacjentom, zarówno tym rokującym powrót do zdrowia, jak i nieuleczalnie chorym, zapewniono opiekę medyczną wraz
z odpowiednią terapią i godne warunki egzystencji. Niemieckie zakłady psychiatryczne budowane od ostatniego dziesięciolecia XIX w. do lat 20.
XX stulecia były ukoronowaniem zarówno dążeń lekarzy, ściśle współpracuj
ących z architektami, do zrealizowania najlepszej tego typu placówki,
jak i konsekwentnej polityki władz w celu utworzenia sieci zakładów krajowych i prowincjalnych. W rezultacie powstały niespotykane gdzie indziej
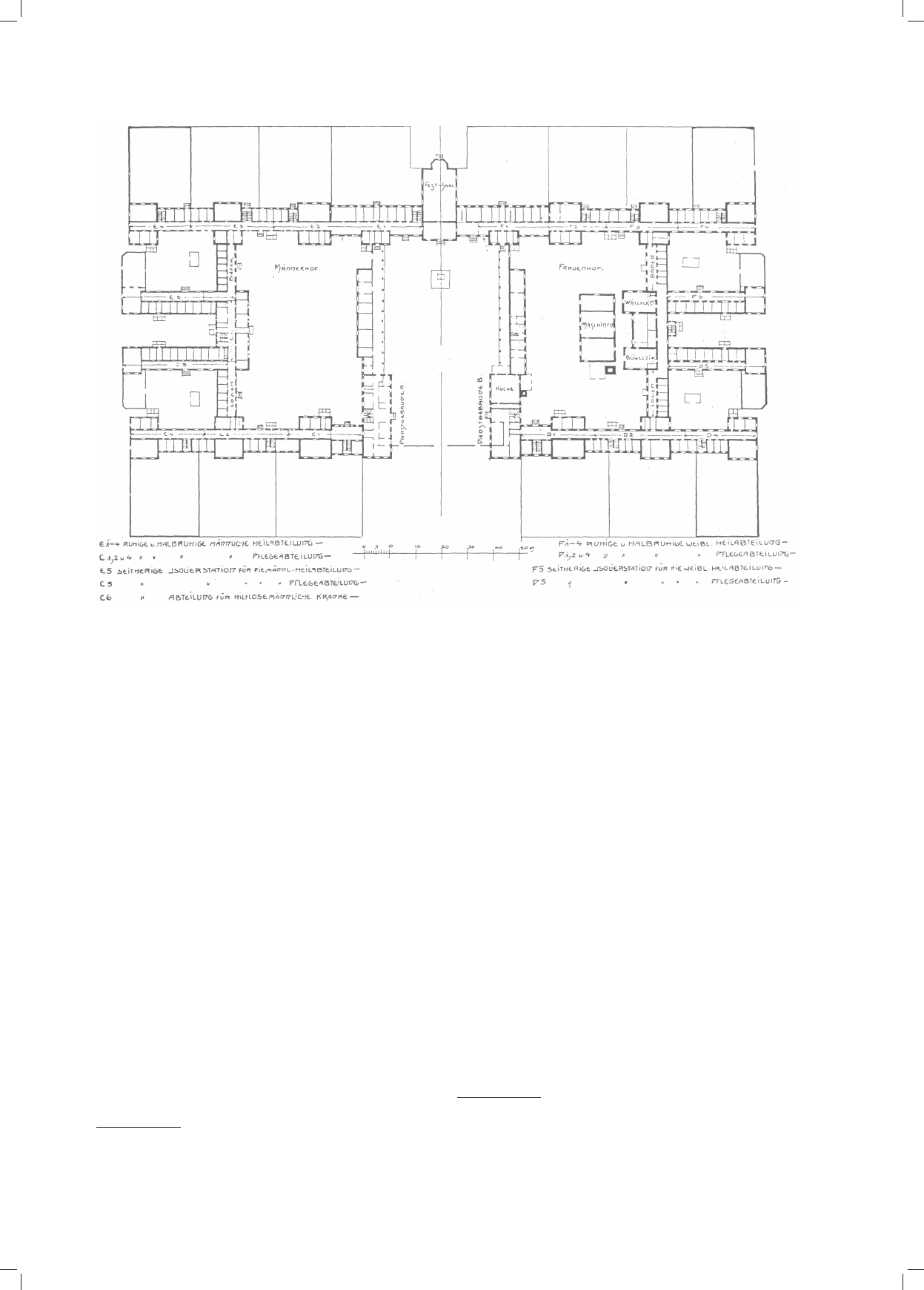
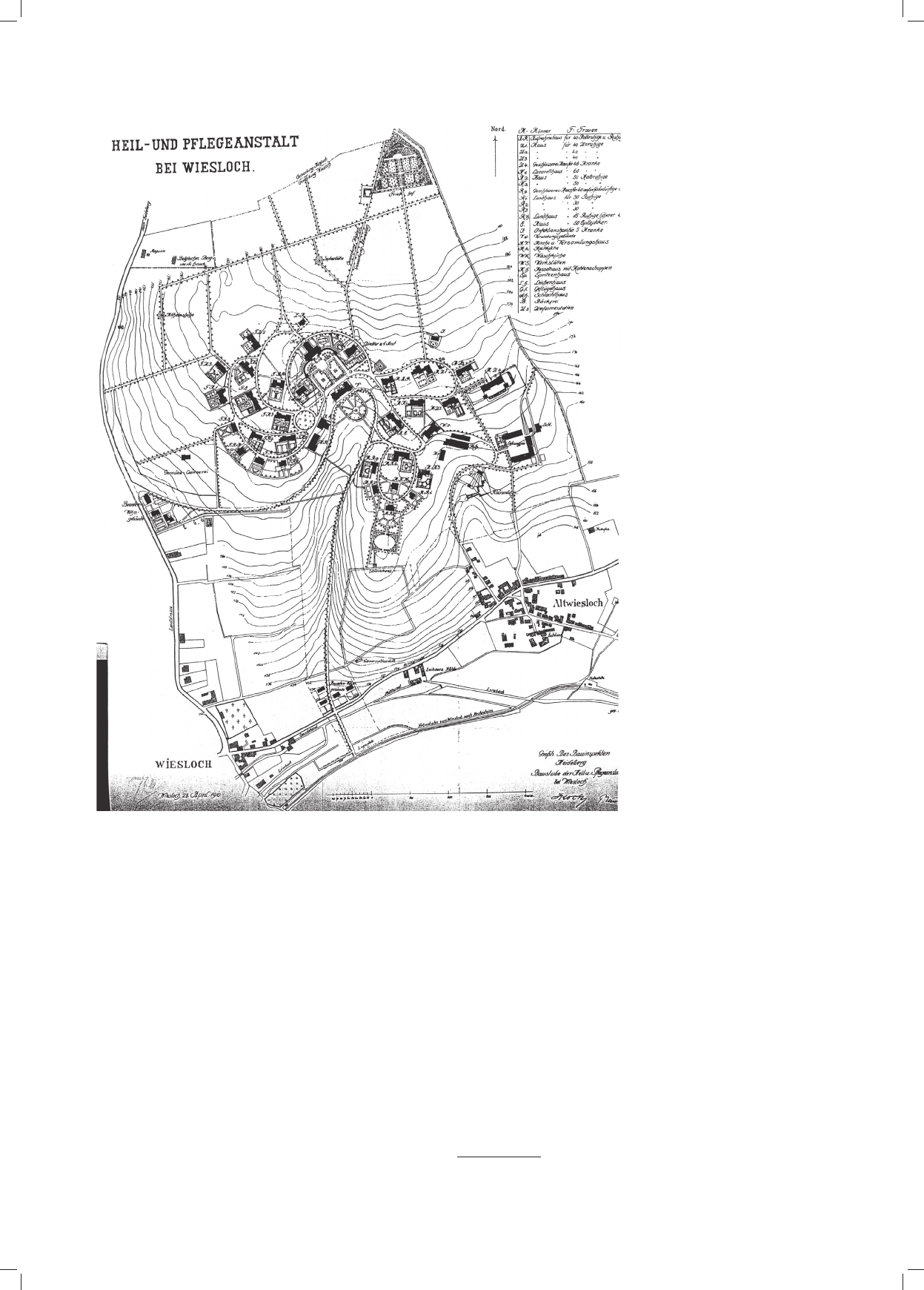
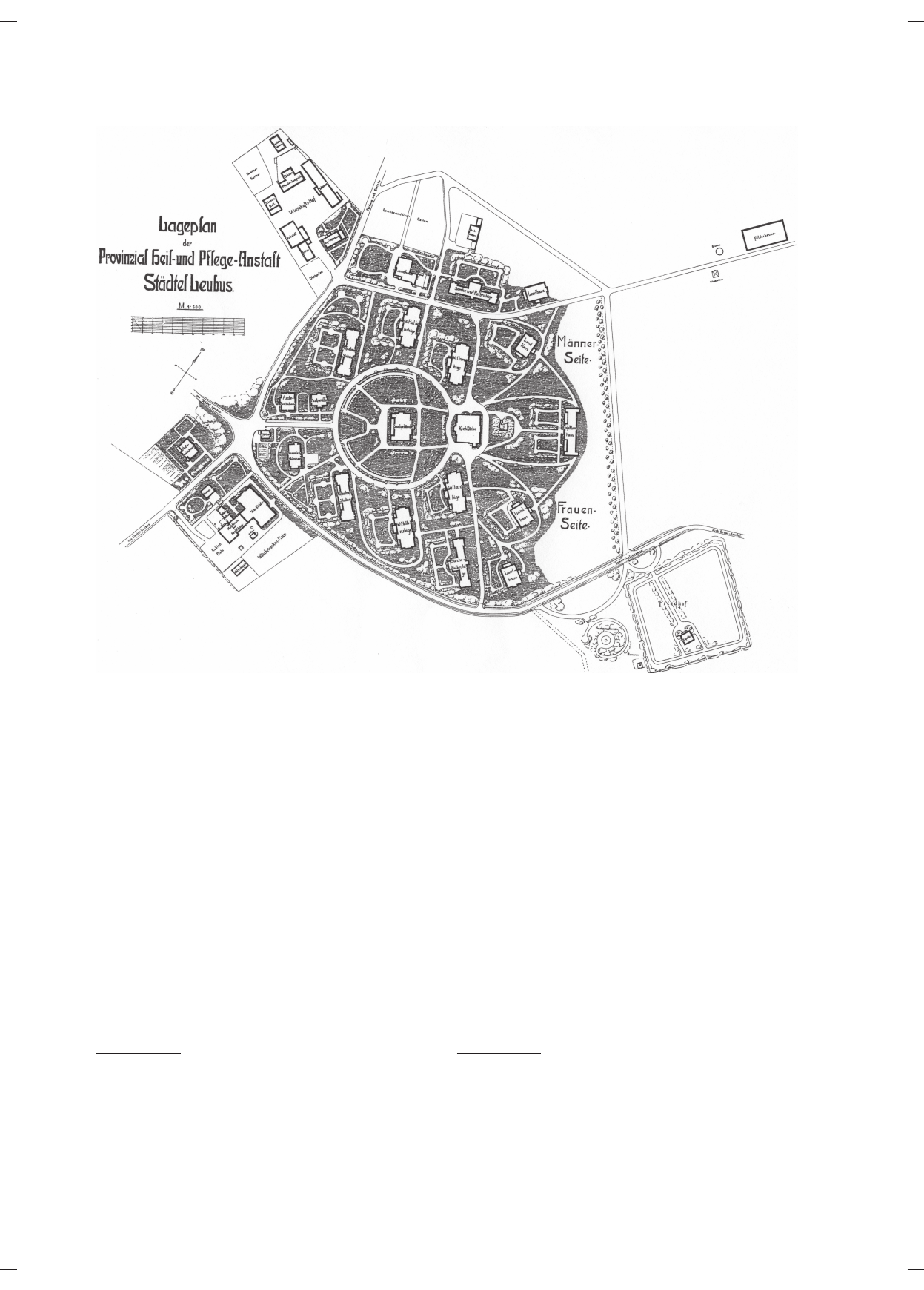
zespoły urbanistyczne. Zaprezentowane w tym artykule jako przykładowe zakłady w Langenhorn, Wiesloch i Lubiążu ukazują związek układu planu,
architektury budynków i założenia parkowo-ogrodowego dostosowanego do ukształtowania terenu z nowymi postępowymi metodami terapii.
Słowa kluczowe: zakłady psychiatryczne, szpitale psychiatryczne, „miasta ogrody”, Langenhorn, Wiesloch, Lubiąż
Abstract
Before the mentally ill, who were considered “unworthy to live”, died during World War II within the Nazis’ “Action T4”, German psychiatry
was famous not only for world-renowned scholars, but also for great mental institutions. They were organized professionally according to the
most recent achievements in that medical fi eld and – in its peak phase – they were uncommonly picturesquely arranged within an urban layout.
Some of them bring to mind the associations with Howard’s movement of Garden Cities, realized in practice in Germany after creating “Deutsche
Gartenstadtgesellschaft” in 1902. Directly, they can be traced to pavilion hospitals, but there is no doubt that they comprised self-suffi cient settlements
with well thought out park sites. It was in such institutions (which resumed their operations after the war) that poorer patients, both showing the signs
of recovery and the terminally ill, were provided with healthcare, including proper therapy and living conditions. German mental institutions built
from 1890
s
to 1920
s
were the crowning achievement of doctors’ efforts, who closely cooperated with architects, in order to build the best facility of
the kind, as well as the result of the consistent policy of the authorities to create a network of domestic and provincial facilities. As a result, unique
urban complexes were created which are not to be found anywhere else. The facilities in Langenhorn, Wiesloch and Lubiąż, presented as examples,
show the connection between the layout, architecture of buildings, and park and garden arrangement adjusted to the landscape of the area with new
progressive methods of therapy.
Key words: mental institutions, psychiatric hospitals, Garden Cities, Langenhorn, Wiesloch, Lubiąż
Bibliografia /References
[1] Ternon Y., Helman S., Eksterminacja chorych psychicznie w III Rze -
szy, PZWL, Warszawa 1974.
[2] „Transferred to Hadamar”. An English Catalogue about the Nazi –
„Eu thanasia”– Crimes in Hadamar, U. Georg, Kassel 2005.
[3] Loose I., Akcja T4. Zbrodnie Akcji „Eutanazja” w okresie naro-
do wego socjalizmu w latach 1933–1945, http://gedenkort-t4.eu/pl/
vergangenheit/aktion-t4 [accessed: 5.01.2015].
[4]
Czyżewski A., Trzewia Lewiatana. Miasta ogrody i narodziny przed -
mieścia kulturalnego, Państwowe Muzeum Etnografi czne, War -
szawa 2009.
[5] Borucka E., W szkatułach zieleni. Europejski ruch miast ogrodów
1903–1930, UW, Warszawa 2014.
[6]
Kiejna A., Wójtowicz M., Prowincjalny Psychiatryczny Zakład Lecz -
ni czo-Opiekuńczy w Lubiążu 1830–1912, Via Nova, Wrocław 2002.
[7] Jetter D., Wichtige Irrenhäuser in Frankreich, Deutschland und
England (1800–1900), „Fortschritte der Neurologie Psychiatrie”
1992, Bd. 60, 337–338.
[8] Jetter D., Grundzüge der Geschichte des Irrenhauses, Wissen-
schaftliche Buchgesellschaft, Darmstadt 1981.
[9] Szumowski W., Historia medycyny, Sanmedia, Warszawa 1994,
636–637.
[10] Brzeziński T., Historia medycyny fi lozofi cznie ujęta, PZWL, War-
szawa 2000, 312–313.
[11] Deutsche Heil- und Pfl egeanstalten für Psychischkranke in Wort
und Bild. Den Mitgliedern des IV. Internationalen Kongresses zur
Fürsorge für Geisteskranke Berlin, den 3. bis 7. October 1910
gewidmet, J. Bres ler (red.), Carl Marhold Verlagsbuchhandlung,
Halle a.S. 1910, Bd. 1.
[12] Vanja Ch., Der Irrenhausgarten als Therapeutikum, „Schriftenreihe
der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Geschichte der Nervenheilkunde”
2006, Bd. 12, 287–312.
[13] „Wochenblatt für Architekten und Ingenieure” 1880, Bd. 2, 197,
202, 217, 235, 260.
[14] Funk A., Irren-Anstalten, [w:] J. Durm, H. Ende, E. Schmitt (red.),
Handbuch der Architektur, Verlag von Arnold Bergsträsser in
Darm stadt 1891, Th. 4, Hlb.-Bd. 5, Hf. 2, 1–59.
[15]
Neuberger T., Staatsanstalt Langenhorn, [w:] J. Bresler (red.),
Deutsche Heil- und Pfl egeanstalten für Psychischkranke in Wort und
Bild. Den Mitgliedern des IV. Internationalen Kongresses zur Für -
sorge für Geisteskranke Berlin, den 3. bis 7 October 1910 ge wid met,
Carl Marhold Verlagsbuchhandlung, Halle a.S., 1910, Bd. 1, 127–140.
[16] Schmiedebach H.-P., Ankele M., Die Irrenanstalt Langenhorn um
1910 – Heilanstalt oder landwirtschaftliche Produktionsstätte?,
„His toria Hospitalium. Jahrbuch der Deutschen Gesellschaft für
Kran kenhausgeschichte” 2012/2013, Bd. 28, 255–268.
[17] Tomaszewicz A., Schulze-Naumburg Paul, [w:] I. Bińkowska,
E. Szopińska (red.), Leksykon zieleni Wrocławia, Via Nova, Wroc-
ław 2013, 890.
[18] Mues A., Eine Gartenstadt für psychisch Kranke. Die Baugeschich -
te der Heil- und Pfl egeanstalt Wiesloch, [w:] J. Weis (red.), Wies-
loch. Beiträge zur Geschichte, Verlag Regionalkultur, Wiesloch
2001, Bd. 2, 289–304.
[19] Eysymontt R., Ilkosz J., Blümner E., [w:] R. Eysymontt, J. Ilkosz,
A. Tomaszewicz, J. Urbanik (red.), Leksykon architektury Wroc ła-
wia, Via Nova, Wrocław 2011, 956.
[20] Kluckert E., Architektura barokowa w Niemczech, Szwajcarii, Au-
strii i Europie Środkowej, [w:] R. Toman (red.), Architektura ba ro -
ku. Architektura, rzeźba, malarstwo, h.f. Ullmann, Wydawnic two
Baran i Suszczyński, Warszawa 2007, 190–191.
[21]
Chrzanowski T., Kornecki M., Sztuka Śląska Opolskiego, od śred nio -
wie cza do k. w. XIX, Wydawnictwo Literackie, Kraków 1974, 362–366.
[22] Alter W., Prowinzial-Heil- u. Pfl egeanstalt zu leubus i. Schl., [w:]
J. Bresler (red.), Deutsche Heil- und Pfl egeanstalten für Psy chisch-
kranke in Wort und Bild. Den Mitgliedern des IV. Inter na tionalen
Kongresses zur Fürsorge für Geisteskranke Berlin, den 3. bis 7. Oc-
tober 1910 gewidmet, Carl Marhold Verlagsbuchhandlung, Halle
a.S. 1910, Bd. 1, 346–350.
[23] Urbanik J., Paul Hatt, [w:] I. Bińkowska, E. Szopińska (red.),
Leksykon zieleni Wrocławia, Via Nova, Wrocław 2013, 871–872.
[24] Fusinger C., Tevaerai D., Lieux de folie – Monuments de raison.
Architecture et psychiatrie en Suisse romande, 1830–1930, Presses
Polytechniques et Universitaires Romandes, Lausanne 1998.