Petrographic,mineralogical,climaticanalyses,riskmaps / Analizypetrograficzne,mineralogiczne,klimatyczne,mapyryzyka 149
Abstract
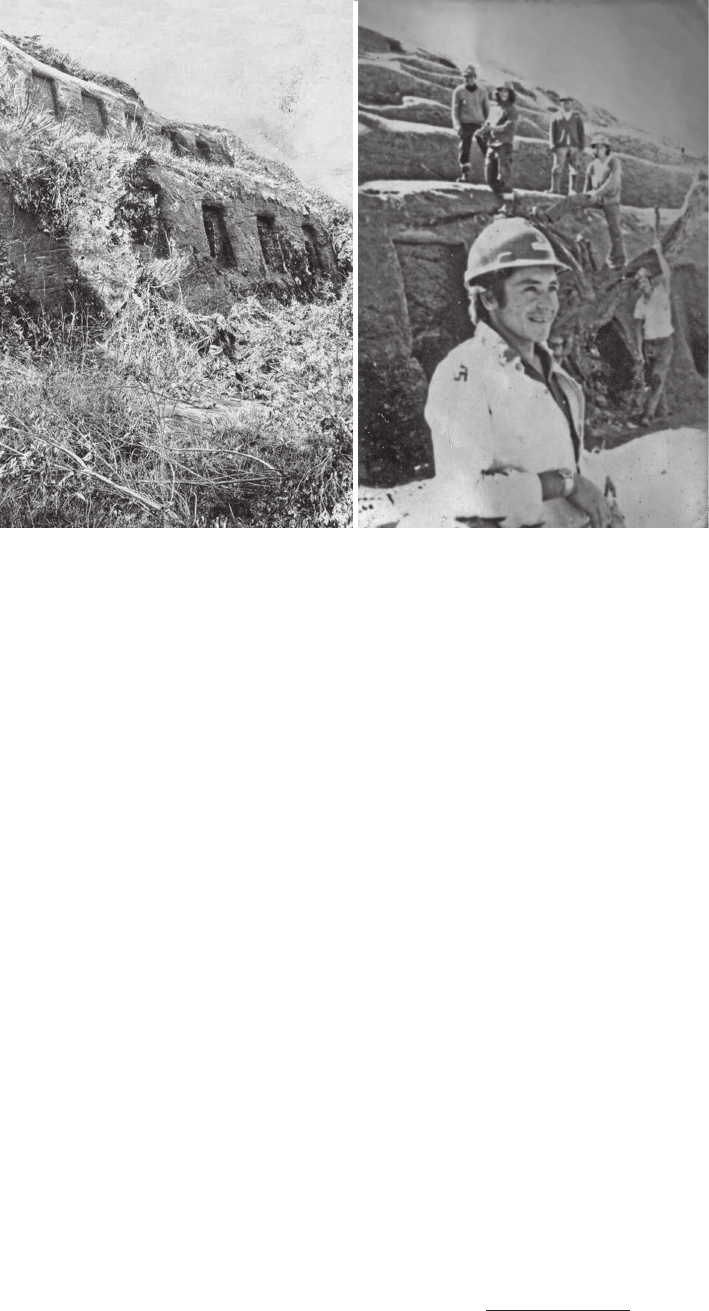
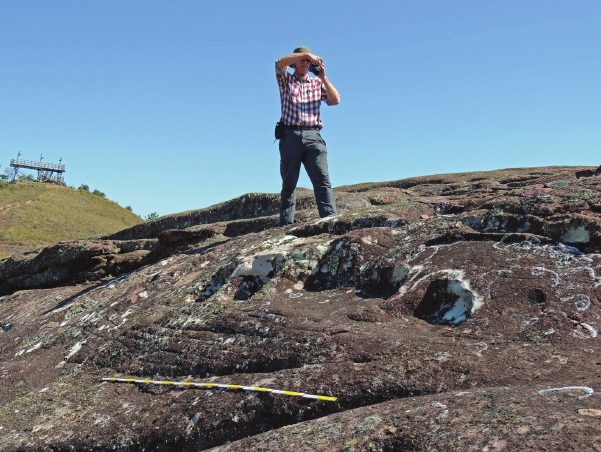
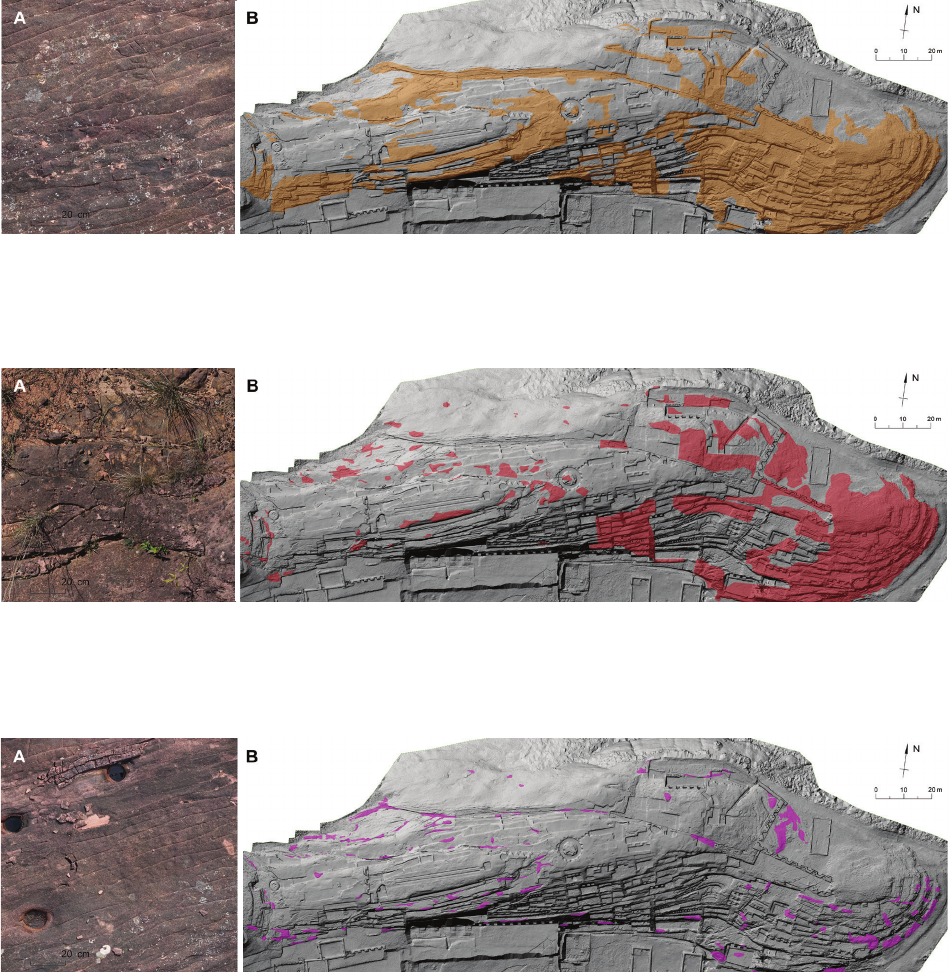
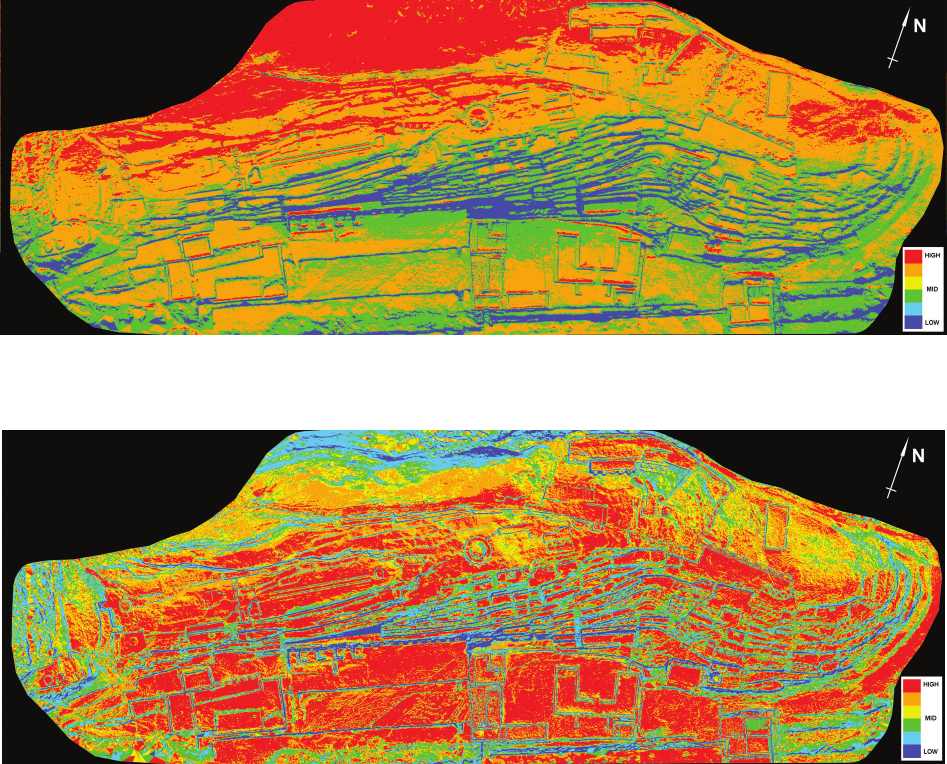
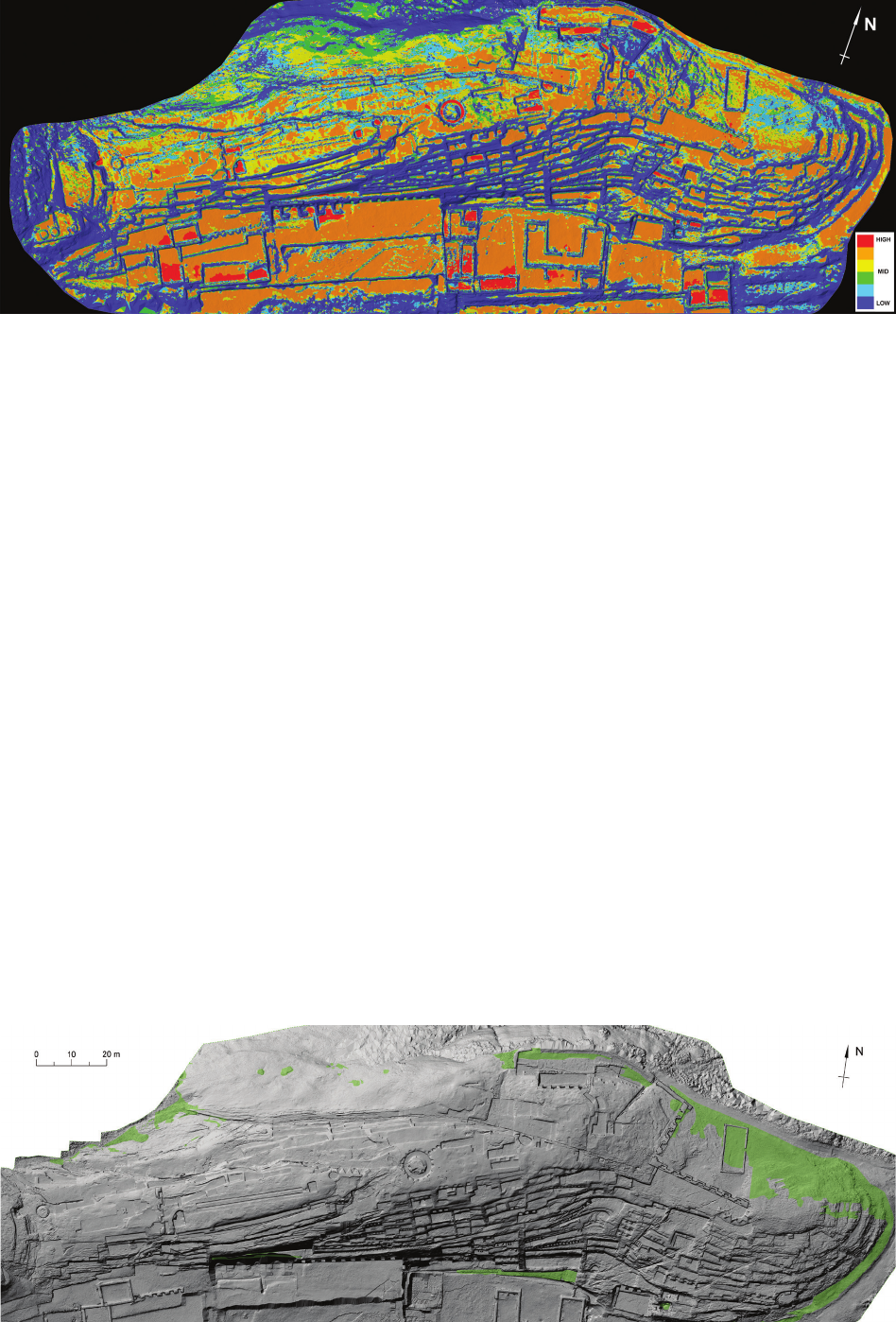
El Fuerte de Samaipata is a pre-Hispanic archaeological site in Bolivia that has been on the UNESCO World Heritage List. Its main part – the rock
– is densely covered with a complex arrangement of terraces, platforms, water reservoirs, channels, and petroglyphs. The rapidly progressing erosion
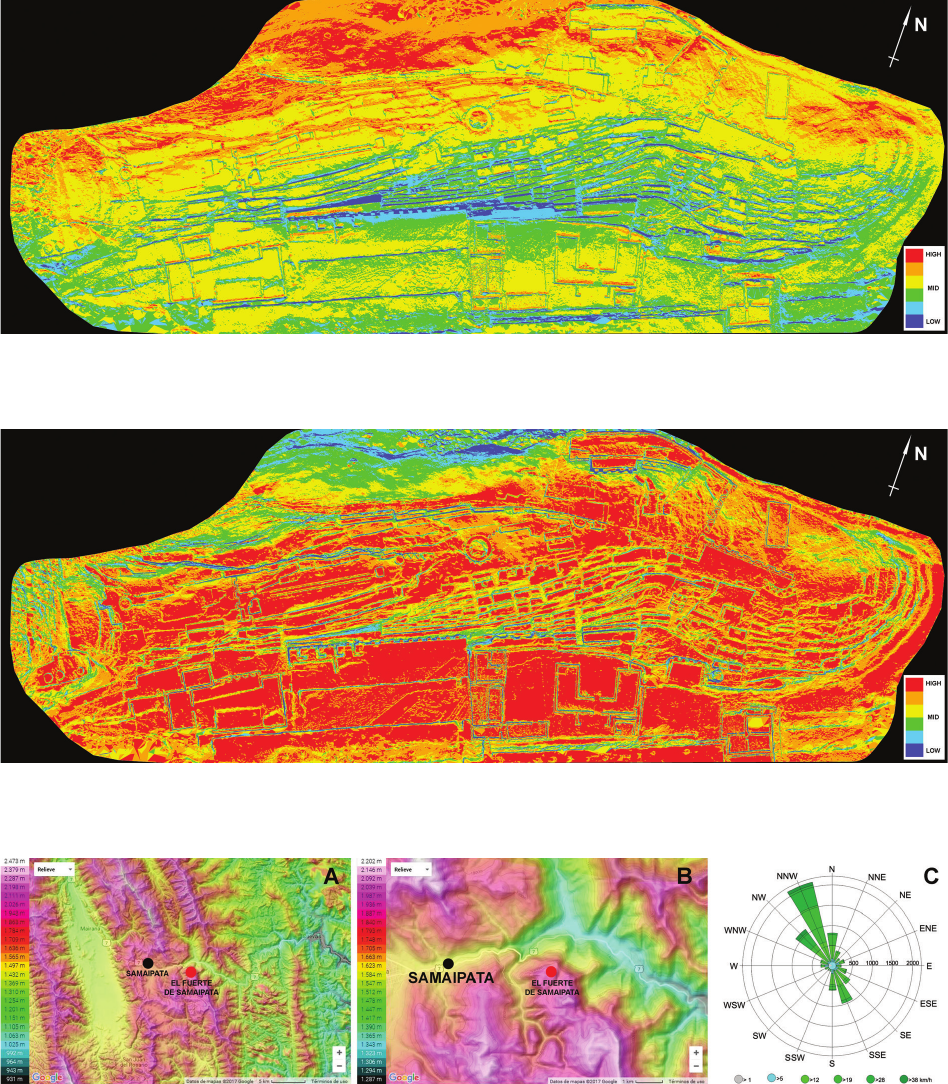
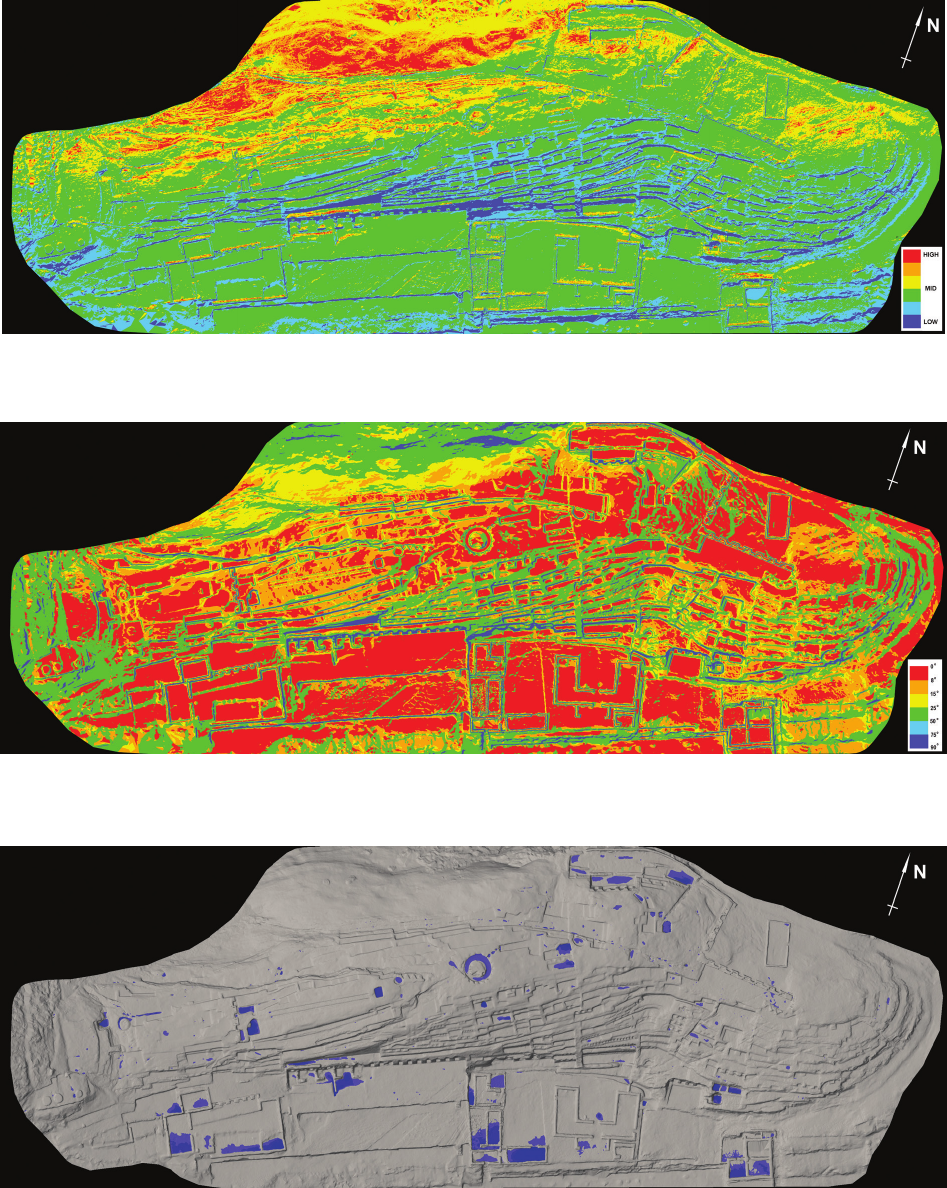
of the rock is making the petroglyphs less and less clear, and some are no longer recognisable. The main topic of this study is to indicate all risk
factors conducive to erosion and to create risk maps identifying the most vulnerable areas that require immediate conservation intervention. Parallel
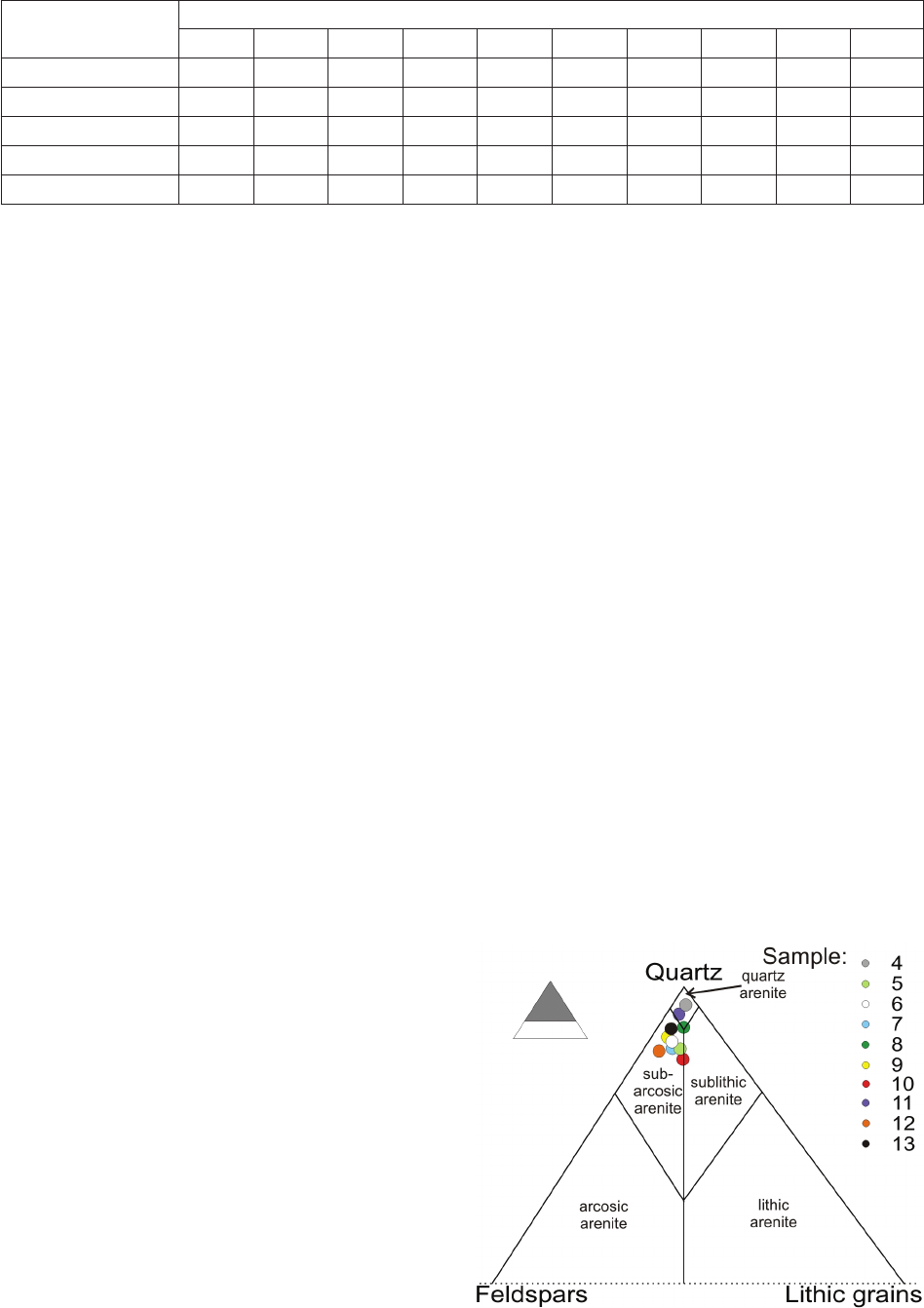
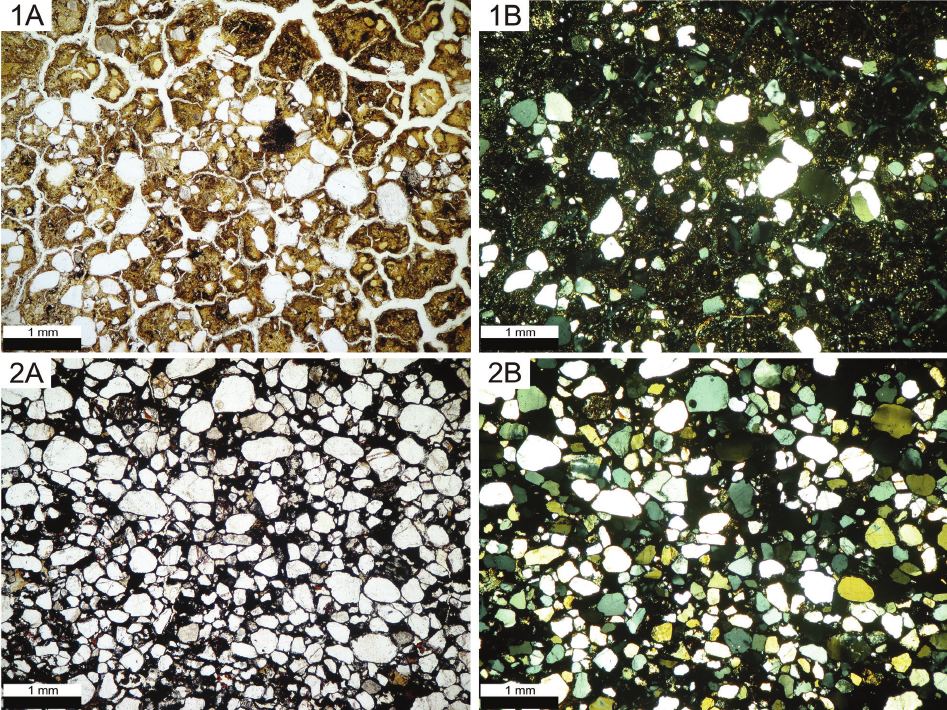
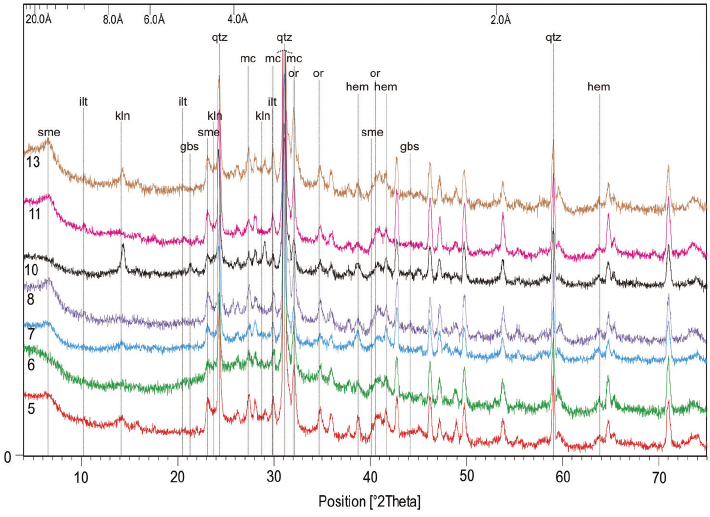
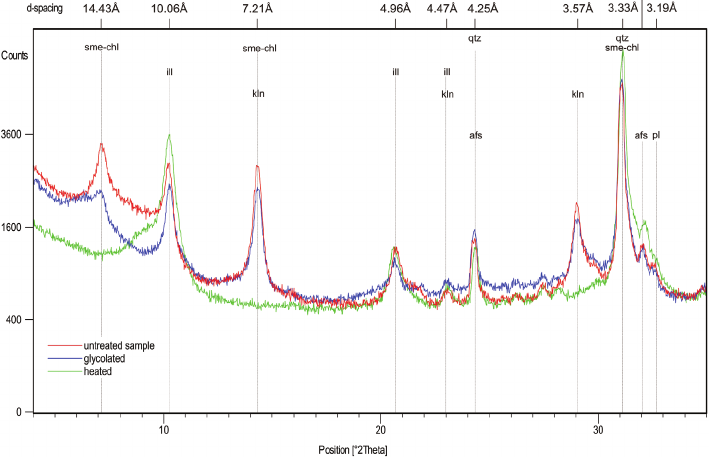
mineralogical and petrographic studies show that the Samaipata rock is a quartz-rich, porous, well-sorted sandstone, classied as quartz arenite
or subarcosic arenite. The cement of the rock is composed of quartz overgrowth and ubiquitous, pore-lling hematite-clay aggregates containing
non-expanding kaolinite, illite, and expanding smectite. The rock exhibits dierent stages of weathering, from relatively fresh to strongly altered and
heavily cracked. In comparison to fresh rock, the latter has cement enriched in clay minerals and is depleted in hematite due to weathering and the
dissolution of the iron-bearing phase.
Key words: Samaipata, conservation, climatic and topographical risk factors, sandstone, mineralogy
Streszczenie
El Fuerte de Samaipata to wpisane na Listę Światowego Dziedzictwa UNESCO prehiszpańskie stanowisko archeologiczne w Boliwii. Jego główna
część to skała ze złożonym układem tarasów, platform, zbiorników wodnych, kanałów i petroglifów. Szybko postępująca erozja sprawia, że petroglify
stają się coraz mniej wyraźne, a niektóre nie są już rozpoznawalne. Głównym tematem badań jest wskazanie wszystkich czynników ryzyka sprzyjają-
cych erozji oraz stworzenie map ryzyka identykujących najbardziej wrażliwe obszary wymagające natychmiastowej interwencji konserwatorskiej.
Badania mineralogiczne i petrograczne wskazują, że Samaipata to bogaty w kwarc, porowaty, dobrze posortowany piaskowiec, sklasykowany jako
arenit kwarcowy lub arenit subarkozowy. Spoiwo składa się z przerostu kwarcu i wszechobecnych, wypełniających pory agregatów hematytowo-
-gliniastych zawierających nierozprężający się kaolinit, illit i rozszerzający się smektyt. Skała wykazuje różne etapy wietrzenia, od stosunkowo świe-
żego do mocno zmienionego i mocno spękanego. W porównaniu ze świeżą skałą ta ostatnia ma cement wzbogacony w minerały ilaste i jest zubożona
w hematyt z powodu wietrzenia i rozpuszczenia fazy żelazonośnej.
Słowa kluczowe: Samaipata, konserwacja, klimatyczne i topograczne czynniki ryzyka, piaskowiec, mineralogia
Acknowledgements /Podziękowania
Thepresentedworkisa partof theresearch projectsponsoredbythe
grant given to the Wrocław University of Science and Technology by
thePolish NationalScience Centre(grant No.2014/15/B/HS2/01108).
Additionally, the municipality of Samaipata, represented by Mayor
FalvioLópesEscalera,contributedtothisresearchbyprovidingtheac-
commodationduringtheeldworkinJuneandJuly2016,aswellasin
July2017.TheMinistryofCultureandTourismofBoliviakindlygrant-
edallnecessarypermits(UDAMNo.014/2016;UDAMNo.060/2017).
The research was conducted in close cooperation with the Centre for
Pre-Columbian Studies of the University of Warsaw in Cusco. Spe-
cialists from many other universities and research centresalso joined
theproject.
[9] Meyers A., Reexiones acerca de la periodización de la Cultu-
ra Inka: perspectivas desdeSamaipata, Orientede Bolivia, [in:]
C. Diez Marín (ed.), ActasdelXIICongresoNacionaldeArqueo-
logíaArgentina, Editorial de la Universdad de la Plata, La Plata
1999, t. 1, 239–251.
[10] El Fuerte de Samaipata: Estudios arqueológicos, A. Meyers,
I. Combès (comp.), Biblioteca del Museo de Historia Universidad
Autónoma Gabriel René Moreno, Santa Cruz de la Sierra 2015.
[11] Combès I., Meyers A., El Fuerte de Samaipata en contexto: Es-
tudios históricos, Biblioteca del Museo de Historia Universidad
Autónoma Gabriel René Moreno, Santa Cruz de la Sierra 2018.
[12] Avilés S., ConservazionedeltempiodellaroccascolpitadiSamai-
pata–SantaCruz,Bolivia(Sudamerica), Tesi di Master: Universi-
tà di Bologna, Sede di Ravenna, Facoltà di Conservazione dei Beni
Culturali, Dipartimento di Storie e Metodi per la Conservazione dei
Beni Culturali, 2002, www.stonewatch.de/media/download/sc%20
04.pdf [accessed: 27.09.2017].
[13] Avilés S., IntroduzioneallaconservazionedellaRocciaScolpitadi
Samaipata, Bolivia, 2011, http://www.rupestreweb.info/samaipata.
html [accessed: 27.09.2017].
[14]
Avilés S., LaconservacióndelaRocaSagradadeSamaipata, [in:]
A. Meyers, I. Combès (comp.), El Fuerte de Samaipata: Estudios
arqueológicos, Biblioteca del Museo de Historia Universidad Autó-
noma Gabriel René Moreno, Santa Cruz de la Sierra 2015, 161–170.
[15] Elsen J., Microscopyofhistoricmortars–areview, “Cement and
Concrete Research” 2006, Vol. 36, Iss. 8, 1416–1424.
[16] Strzelczyk A.B., Karbowska-Berent J., Drobnoustroje i owady
niszczącezabytkiiichzwalczanie, Wydawnictwo Naukowe UMK,
Toruń 2004.
[17] Pettijohn F.J., Potter P.E., Siever R., Sand and sandstone, Springer-
Verlag, Berlin–Heidelberg–New York 1972.
[18] Földvári M., Handbook of thermogravimetricsystem of minerals
and its use in geological practice, Magyar Állami Földtani Intézet
(Geological Institute of Hungary), Budapest 2011.
[19] Wyrwicki R., Analiza derywatograczna skał ilastych, Wydaw-
nictwo Uniwersytetu Warszawskiego, Warszawa 1988.
[20]
Łukaszewicz J.W., Rodzajekamienisztucznych,właściwościorazod-
pornośćnadziałanieczynnikówniszczących, [in:] W. Do ma słowski
(red.), Zabytki kamienne i metalowe ich niszczenie i konserwacja
prolaktyczna, Wydawnictwo Naukowe UMK, Toruń 2011, 47–87.