8 Bogna Ludwig
Froberg in Nuremberg
9
[26]. Böckler’s work on the con-
struction of hydraulic systems and numerous examples
of implementation [27] was also familiar. In the compo-
sition of Silesian fountains and the form of sculptures, we
usually observe creative combinations of elements taken
from various models.
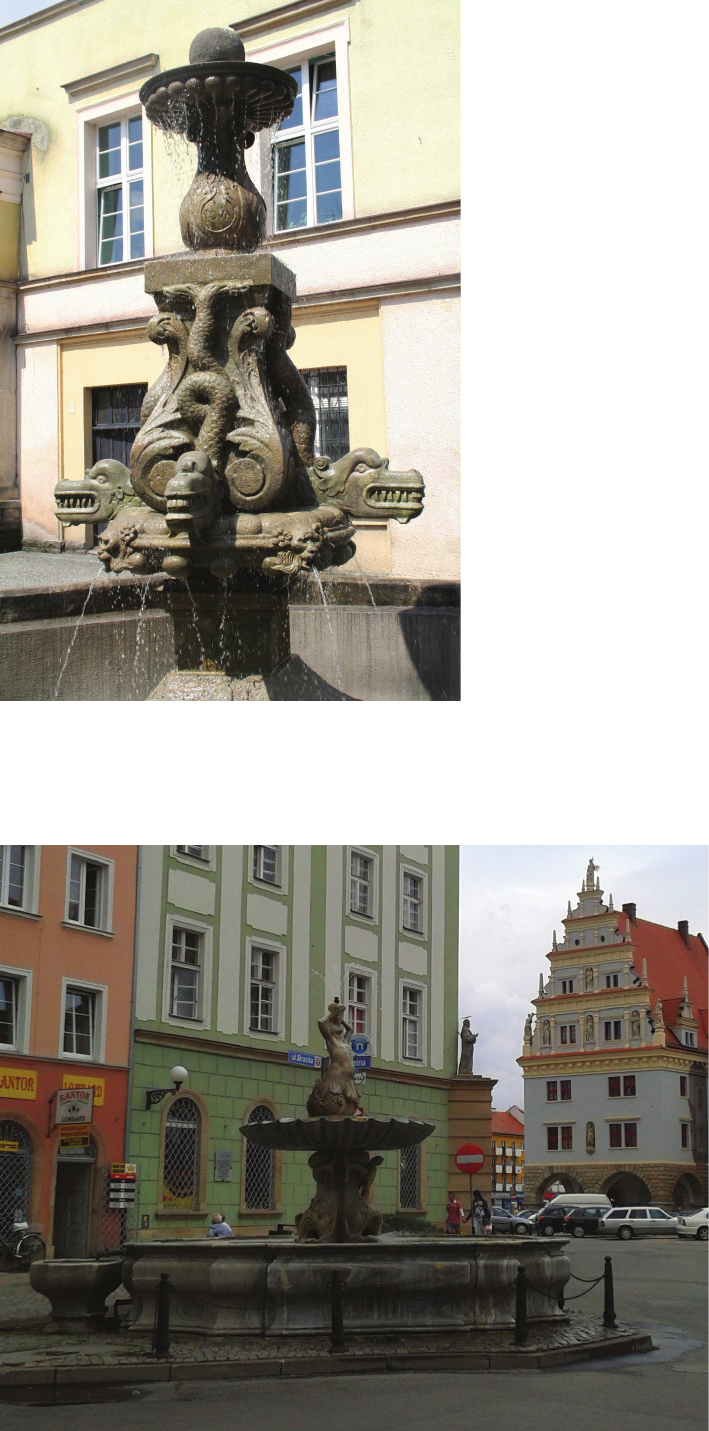
All Silesian urban fountains of the Renaissance and
Baroque periods were made of stone; it was sandstone, ex-
cept for the fountain in Nysa which was carved in Sławnio-
wice marble, from a quarry close to the town. They are of
comparable size, with the height tting the ground oor
of the buildings, from about 3 to 5 m. Only the Wro cław
fountain was twice as big, as was the column of St. Ma-
ternus in Lubomierz.
From the beginning, the two most common forms of
fountains were used alternately. The one with a shaft sup-
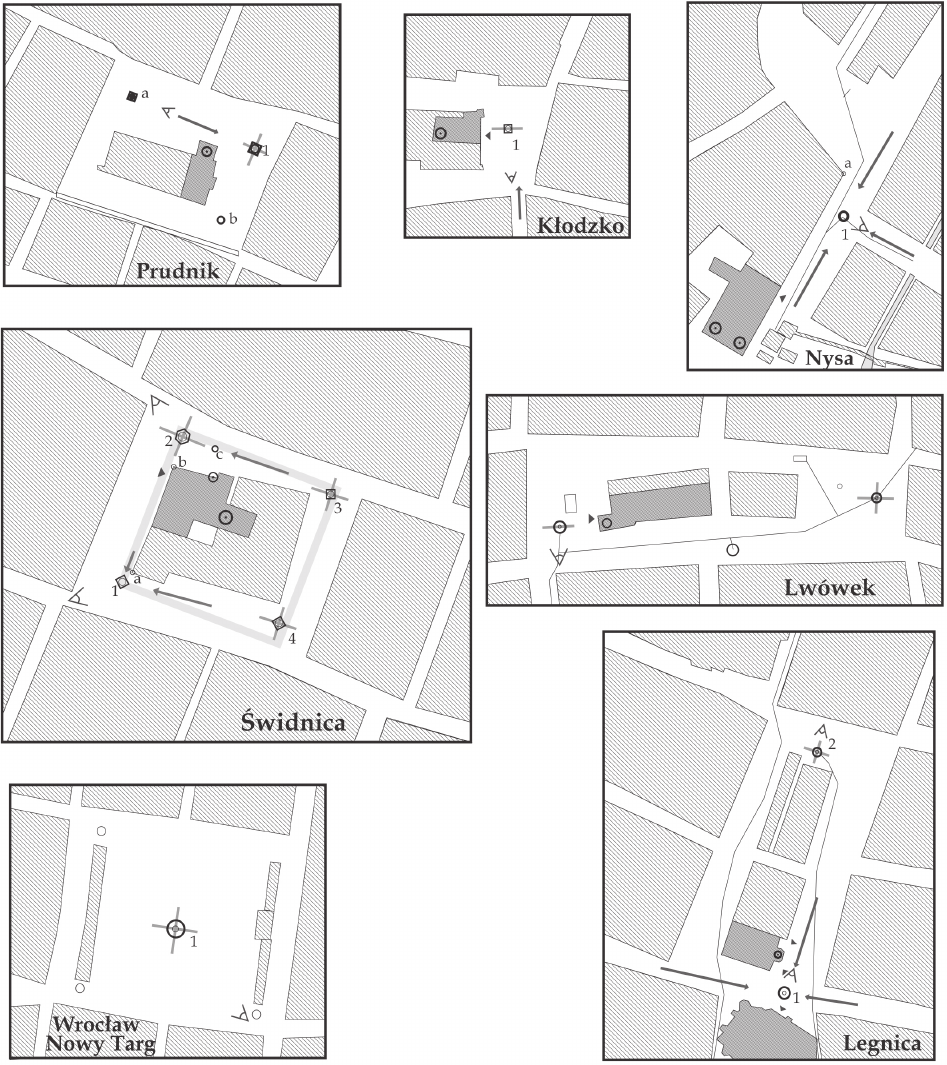
porting a canopy was used in Złotoryja, Prudnik, Kłodzko,
Nysa and in the last two simple fountains in Świdnica. The
candelabra shafts were decorated with images of dolphins
(Złotoryja, Kłodzko) modelled on the fountain del Trullo
(1572) – the oldest modern fountains in Rome, replicated
in Böckler’s designs [27, V. 3, vol. 96, 110, 111, 119] – or
of atlantes (Prudnik), the likes of which we can see on
the fountain dei Tritoni in Piazza della Bocca della Verità
[27, V. 3, vol. 86, 99]. In the simplest solutions it was only
covered with ornamental decoration (Neptune’s Fountain,
Świdnica). The Świdnica Atlas Fountain stands out, hav-
ing a gure supporting a bowl set on a high pedestal. Only
the largest fountain in Wrocław uses a more ornamented
and elaborate form, referring to arrangements with a can-
delabra body, possibly inspired by the Salzburg fountain
(Residenzbrunnen), the earliest Renaissance fountains of
Orion in Messina by Montorsola or Neptune in Naples, or
illustrations by H.V. de Vries. The shaft of the Wrocław
fountain had a base decorated with representations of at-
lantes, nereids and caryatids carrying a bowl, in which
a three-storey pedestal was inserted, impost of a pillar,
decorated with dolphins (and other animals?) under the
main gure
10
. All fountain bowls were shaped quite sim-
ilarly as stylised shells such as a section of a sphere with
a grooved surface, sometimes topped with a circumfer-
ential ring (Złotoryja, Kłodzko). Though the Nysa Triton
Fountain was based on a Roman design, it did not include
the naturalistic version of two shells.
The second solution consisted in placing a single sculp-
ture or a group of sculptures on a pedestal in the middle
of the basin, in which water outlets were installed. The
pedestal could be low, concealed behind the frame of the
basin, as in the Florentine Neptune Fountain (Szprotawa,
both fountains in Legnica). Böckler’s work shows such
solutions on examples of garden fountains [27, V. 2, ta-
bles 41–50]. High pedestals were also used, reminiscent
of solutions from Augsburg fountains (Świdnica – At-
las and Neptune Fountain [27, V. 3, tables 90, 105 and
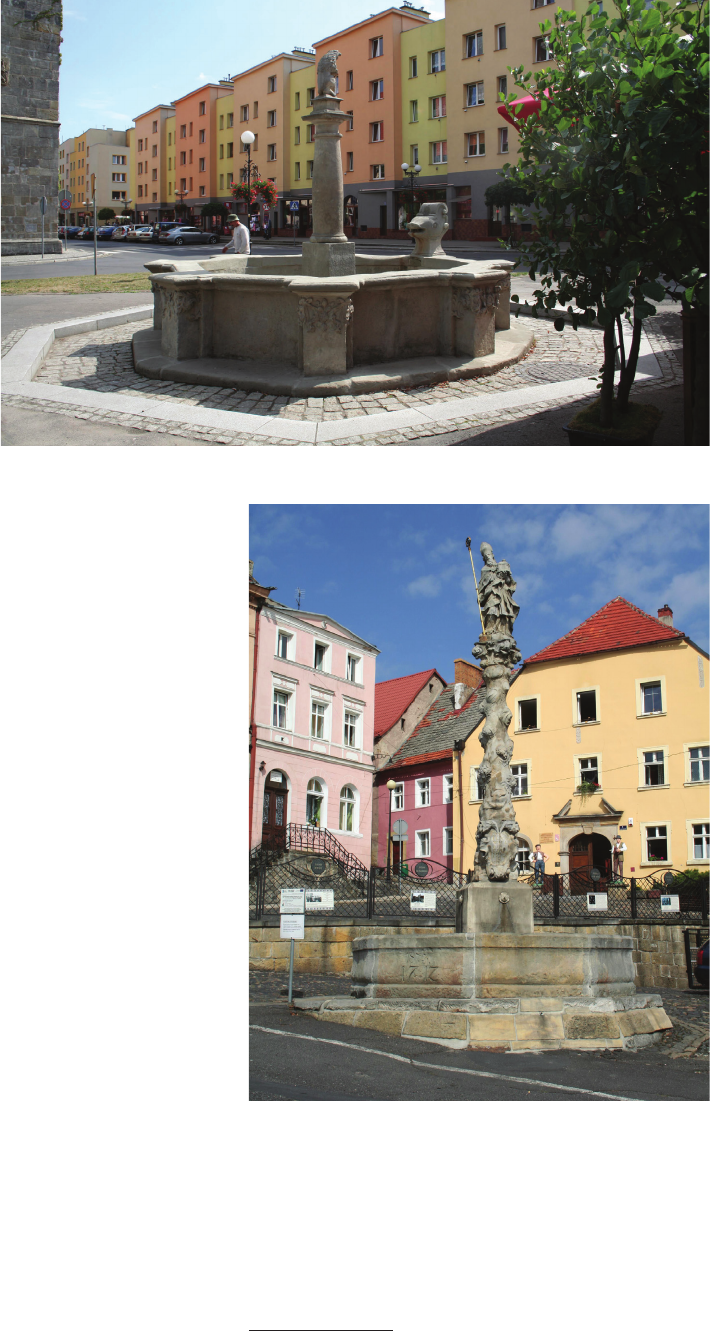
106]), sometimes even in the form of a column (Lwówek,
9
Several copies have been preserved in Wrocław’s libraries.
10
No buttresses were used in the form of a grottarusticaas in the
solutions of the Rezidenzbrunnen fountains in Salzburg and Parnas in
Brno.
Lubomierz). Such fountains in the form of columns were
rare in those times in Central Europe, an example being
the Renaissance Jupiter column in Linz.
The basins were given a quadrilateral outline, a square
with added semicircles known from the pattern of H.V. de
Vries [28] and Böckler [27, V. 2, Table 69, 68, 74]. The
earliest ones, from Złotoryja and Szprotawa, had simpler
octagonal outlines. In Lubomierz and the Neptune Foun-
tain in Wrocław and Świdnica this simple shape was re-
tained. The latest basin in Lwówek Śląski, modied after
the middle of the 18
th
century, was also geometrised. Only
the one in Nysa was a more sophisticated, i.e., the origi-
nally designed outline with concave curves. The linings
of the basins had varied forms, from simple walls with
a protruding sill to richly proled ones with a raned sar-
cophagus cross-section (Nysa).
Hydraulic systems were probably relatively simple
11
.
They used concentrated streams of water directed upwards
or sideways in various directions, sometimes slightly an-
gled downwards. The layout probably was based on the
ideas taken from Böckler’s work [27, V. 1, vol. 1, 5, 6].
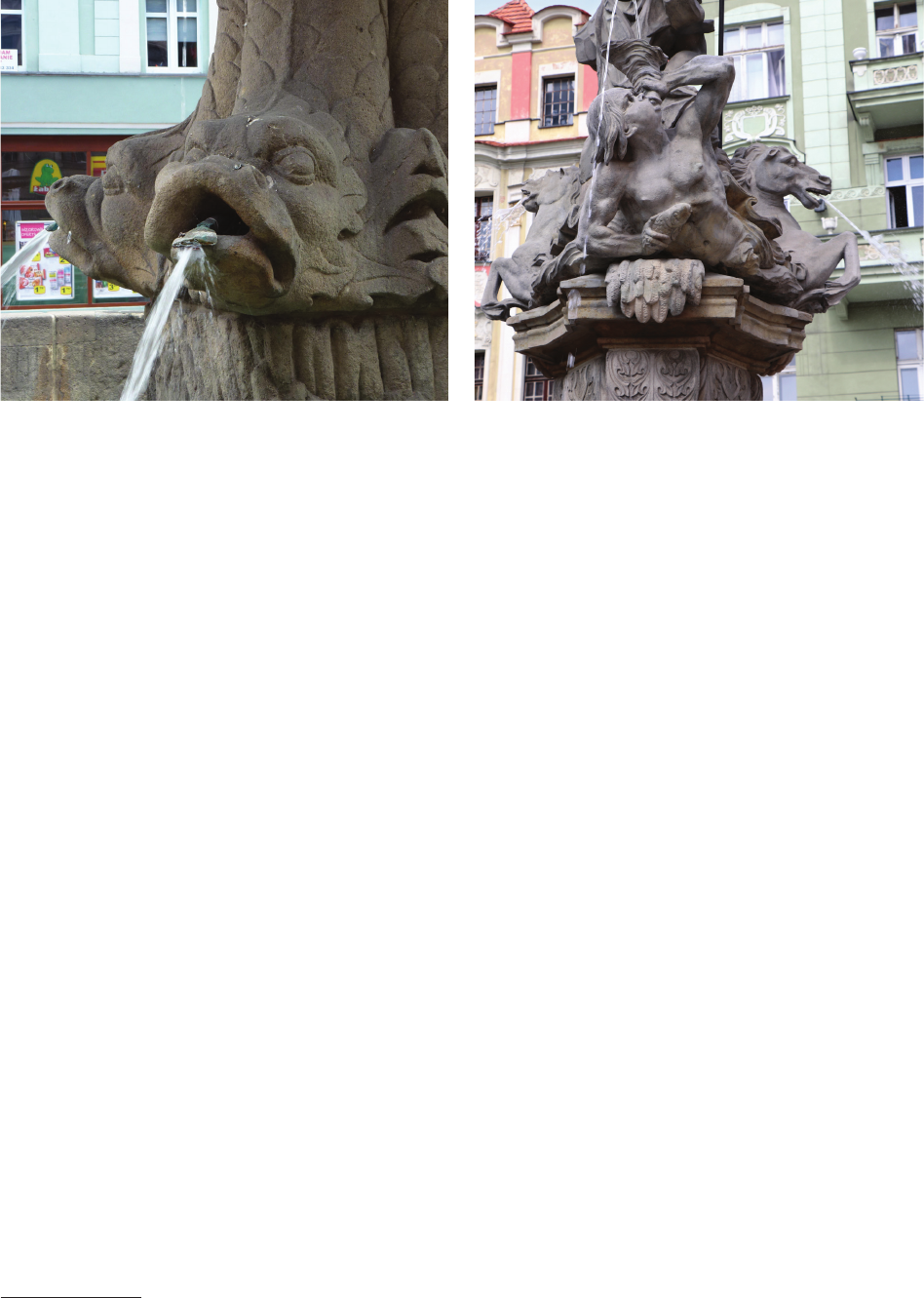
Water was most often ejected from various types of taps
placed in the mouths of mascarons (Złotoryja, Prudnik,
Kłodzko) (Figs. 9, 10), mouths of dolphins (Złotoryja?,
Kłodzko, Nysa, Legnica, Wrocław) and directly installed
in the walls of pedestals (Lubomierz, Świdnica). The water
then owed o the edges of the conches. Nozzles eject-
ing water in a single stream were also located in the main
sculptures crowning the fountains – in the mouths of the
lions in Kłodzko and Lwówek Śląski, in the mouths of the
triton and siren in Nysa and Legnica
12
, and in the beak of
a dove with an olive branch in Prudnik
13
, or in the mid-
dle of the upper bowl (Atlas Fountain). There were also
problems with obtaining the appropriate pressure, as men-
tioned by Zimmermann in relation to the Neptune Foun-
tain in Wrocław [4]. This probably also limited the eects
achieved by the fountains.
Emphasis was laid on the decorativeness of the foun-
tain-cum-monument ornamented with streams of water.
Attention was paid to the quality of the sculpture. They
were ordered in sculpture (e.g., G.L. Weber in Świdnica)
(Figs. 5, 6, 10) and stone workshops (J.A. Karinger) that
were the best in the neighbourhood. In spite of that, none of
the makers put their signature on these works (in contrast
to, e.g., the sculptor from Gdansk, Michael Mandik in Olo-
mouc). The most modest are the sculptures of heraldic an-
imals – lions, made as typical shield holders. The
statue of
St. Maternus from the fountain in Lubomierz, un-worked
from the back side, may suggest a sculpture made for
church decoration. Weber’s sculptures present the highest
level. The more than life-size monumental gure of Atlas
(approx. 2.5 m) [27, V. 3, vol. 93] is characterised by rea-
lism and expression; the highly decorative drapery sur-
rounding the sculpture ensures the impressive form of the
11
All were altered in the 19
th
century.
12
The water features of Neptune’s trident in Wrocław and Legnica
were probably installed in the 19
th
century.
13
In 1853, the imperial eagle was inserted. In the 1960s it was
removed. After a restoration in 1995, it returned in the nial [15].