UrbandevelopmentinGhent / RozwójGandawy 39
tex tile sector hardest, with a lot of manual work being
moved to low-wage countries. Even the UCO (Union Co-
tonnière), once a ourishing textiles group, fell on hard
times. The decline in transit trac, in the wake of the oil
crisis, also dealt severe blows to the port in Ghent. All at
once, Ghent found itself with a surplus of industrial equip-
ment. A museum was founded in 1978 at the city archive
to collect relics of Ghent’s industrial past.
It was some time before the Museum of Industrial Ar-
chaeology and Textile (MIAT), the forerunner to today’s
Museum of Industry, found a home of its own. What does
a collection of this kind entail? And where should it be
housed? Before an answer was found to these questions,
temporary exhibitions were held in various cultural and
historic buildings in the city. A home was nally found for
the museum in 1991, in the former Desmet-Guequier cot-
ton spinning mill on the Minnemeers in Ghent, where it is
still located today. The building is on the border between
the mediaeval city centre and the 19
th
century suburbs, in
the area that forms the transition between the city and the
port area.
Given the importance of the textile industry for Ghent
and the surrounding region, the museum concentrated on
that branch of industry when it built up its collection be-
tween 1978 and 1989
3
. In the 1990s, however, its focus
widened to encompass the material culture of industrial
society in broader terms. The expansion of the collection
was focused more on the acquisition of objects than on
the development of themes. Most of these objects were
acquired passively as donations, rather than by actively
purchasing missing links. Forty years of collecting has
resulted in a rich and diverse group of sub-collections,
covering the history of textile production as well as areas
such as printing, energy services, the metal industry and
machine construction [2].
Who takes care of the big stuff?
There are two separate Flemish ministries with the au-
thority to protect heritage. The Ministry of Environment
and Planning has the authority to protect monuments and
buildings (immovable heritage). The Ministry of Culture
has the authority to protect movable and intangible herit-
age. When it comes to preserving industrial heritage, this
articial division often provokes challenging disputes.
Is a stationary steam engine movable or immovable? Is
a gantry crane on tracks in the docks movable or immova-
ble? Are massive fermentation tanks at a brewery immov-
able by application? In short, who takes care of “the big
stu”?
In Belgium and Flanders, besides private collectors and
enthusiasts, it is mainly small, local organisations that take
care of the preservation and maintenance of large-scale in-
dustrial and technical heritage. The permanent sta who
look after the collections are often supported by dedicated
3
The museum houses the oldest spinning mule still in working or-
der. This semi-automated cotton spinning machine has been on the list of
Flemish Community Masterpieces since 2010.
volunteers, many of whom are retired [3]. The latter bring
their lifetime of accumulated knowledge from an active
career related to the subject of their current passion. They
are connected to a specic museum, location, installation
or type of heritage that they know through and through.
The commercial pool of restorers interested in large tech-
nology heritage is small. Commercial restoration of large,
working industrial heritage, such as stationary steam en-
gines, is almost non-existent. The lack of a commercial
option forms an obstacle to the further preservation, or
sustainable preservation of knowledge about the preser-
vation – and ideally the restoration – of large technology
heritage. This lack also complicates the redevelopment of
de-industrialized sites that have been abandoned for some
time. Private owners and project developers hesitate to
get involved, although they do react positively to the idea
of keeping the machines or installations on site. They en-
counter diculties in nding the right expertise, whether
in terms of project and nancial planning or appropriately
skilled manpower.
Adaptive reuse, or the appreciation of large technology
heritage in public space, changes over time. It tends to
be sensitive to trends, and if it is not thought through, it
may be poorly received by the public. This specically
applies to large machines that were not initially designed
for outdoor use. Erected at important road intersections,
they are intended as monuments or landmarks, promoting
an active industry by creating a link with a nearby city
or a long and glorious industrial history. Unfortunately
this “roundabout heritage” quickly deteriorates, due to an
under-estimation of the costs of periodic and long-term
maintenance, or because of vandalism.
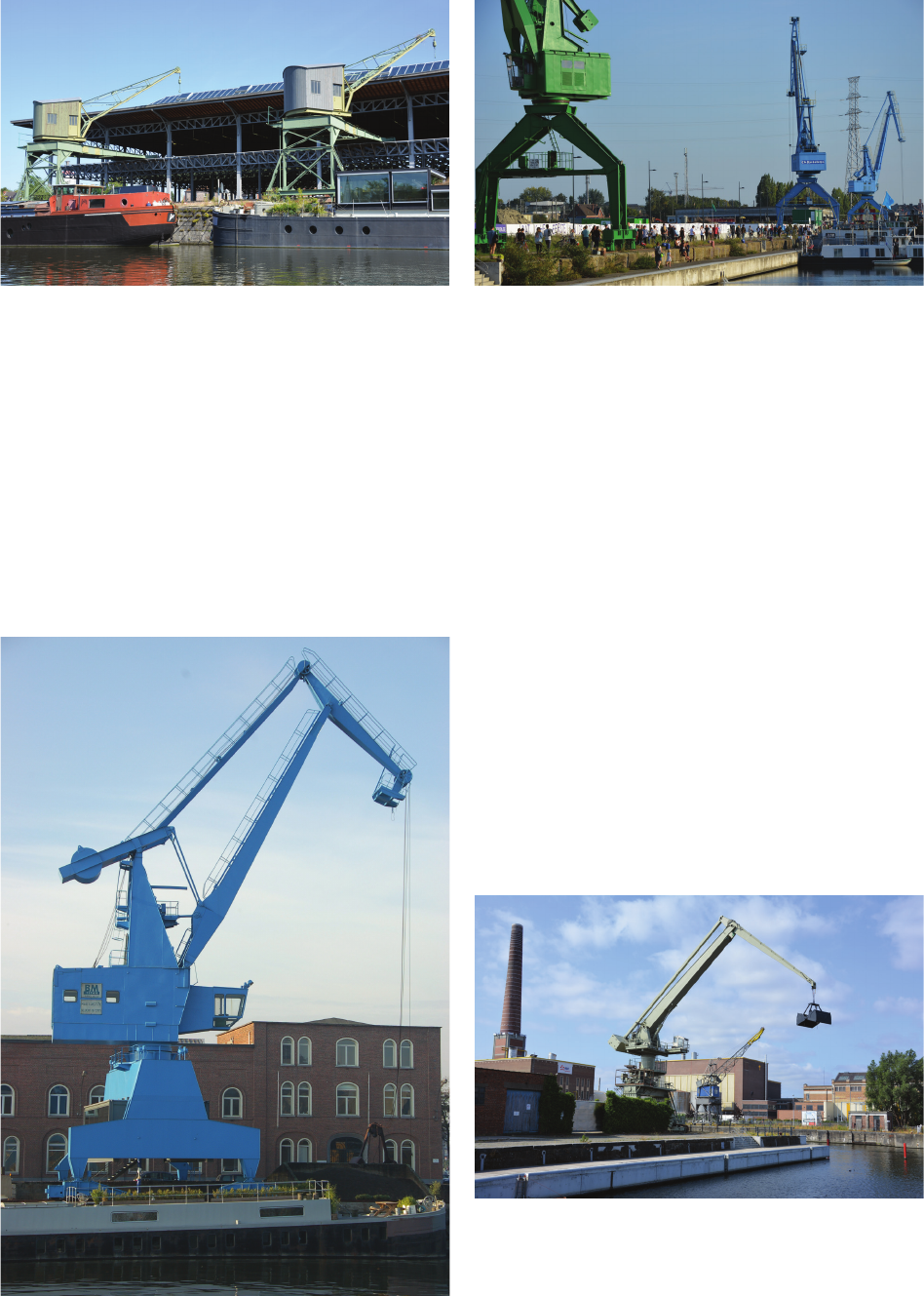
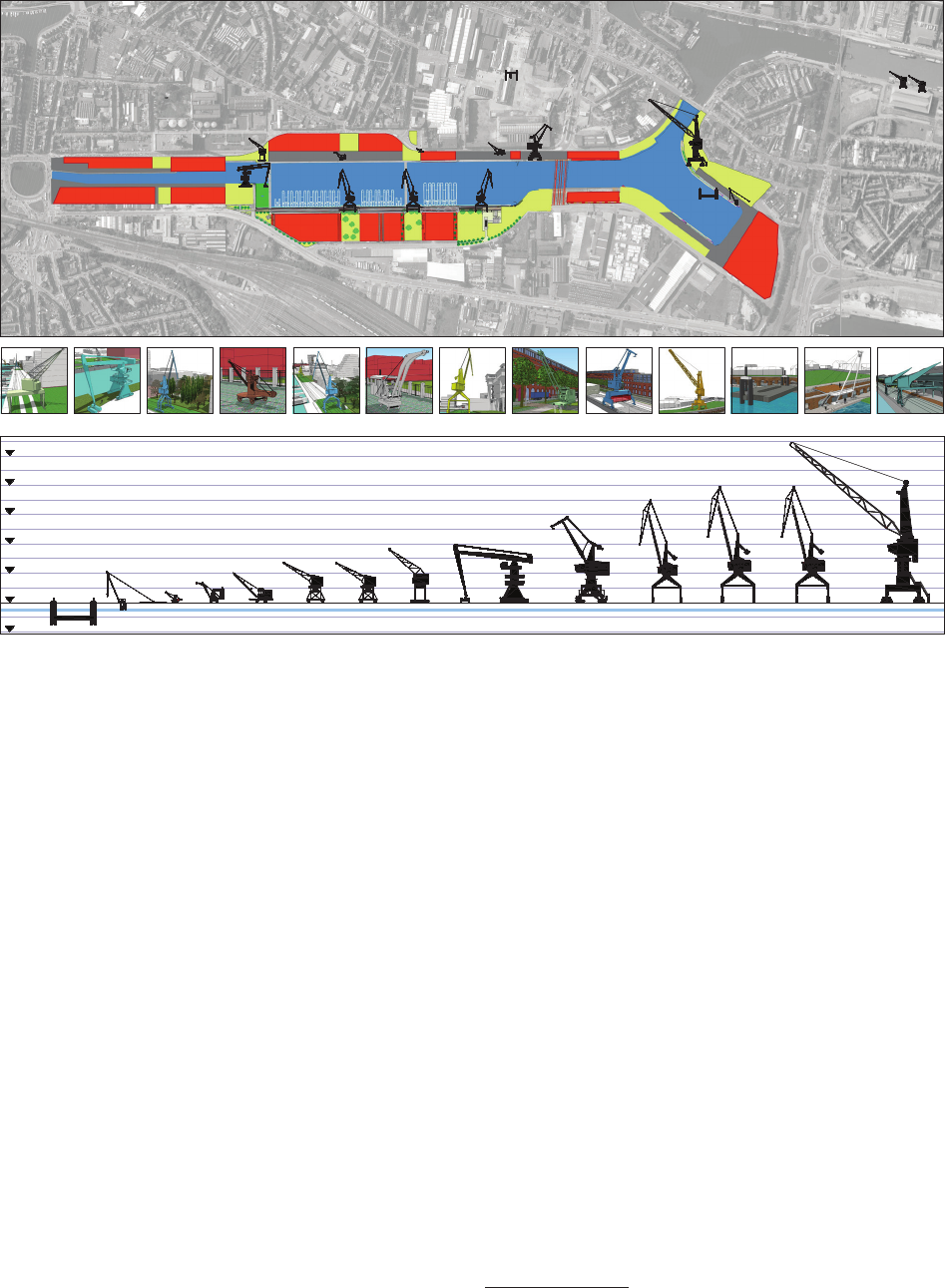
Large technology heritage can also prove challeng-
ing for museums. The mere size of some of these pieces
means that they may literally weigh on the storage fa-
cilities. Stripped of their context or taken out of their
original environment, they tend to be dicult to integrate
into museum exhibitions or projects. This was the case
for a crane donated to the young MIAT during the period
when industry started moving away from the 19
th
century
port. At that time, in contrast to cities like London and
Antwerp, Ghent lacked a vision for port or maritime her-
itage. Moreover, the outside world experienced the sea
port of Ghent as a remote closed-o area with no real
link to the popular, mediaeval city centre. People only
went there if they needed to. Concerned about the possi-
ble loss of important heritage, the museum accepted the
gift of a crane from La Floridienne, a company trading
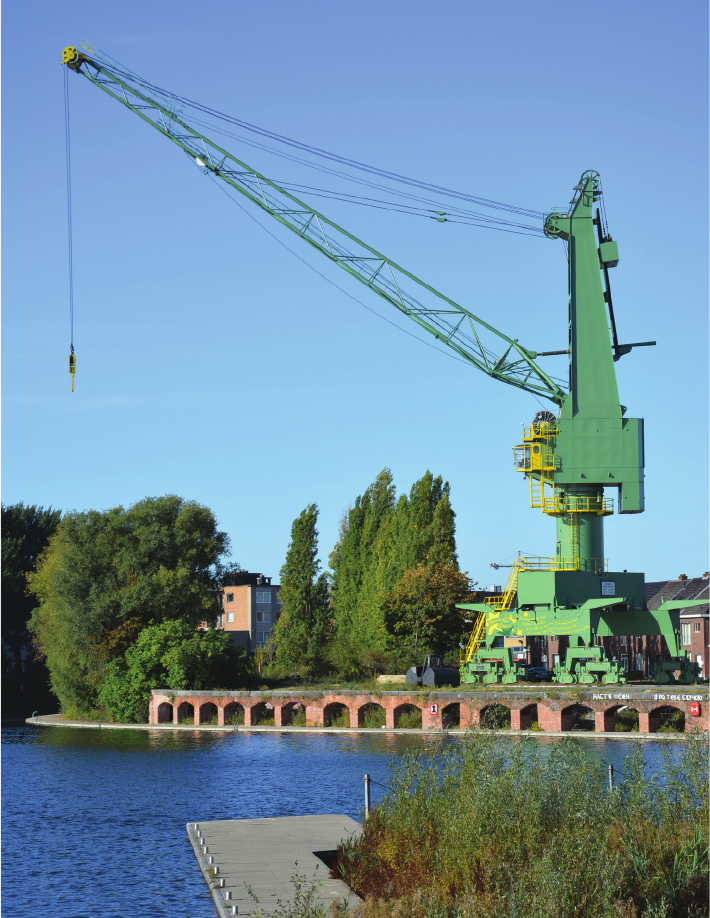
in fertilizers and chemicals. The “Titan” crane rests on
a high portal or gantry section, wide enough to allow two
railway trains to pass underneath, side by side. Origi-
nally commissioned by the city port authorities in 1925,
and constructed by the Antwerp company Titan Anver-
sois, the crane had had an active career on several quays.
However, an inspection revealed that the gantry section
had been damaged by years of exposure to corrosive fer-
tilizers. It was beyond restoration or repair, and scrapped
for safety reasons. A lack of funding and changes in pol-
icy meant that the original plans to erect the crane in the
museum garden, as an eye-catcher and a reference to