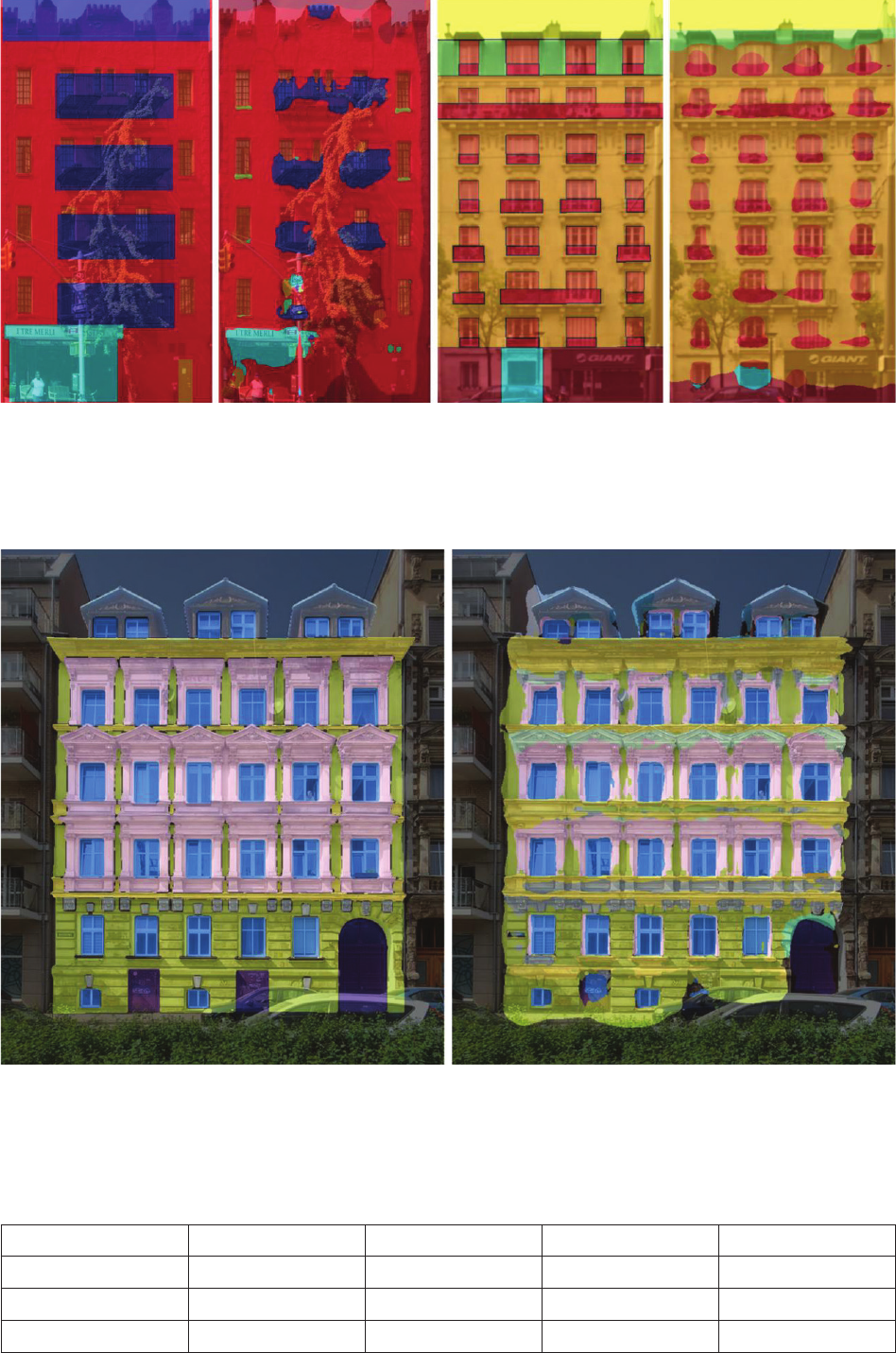
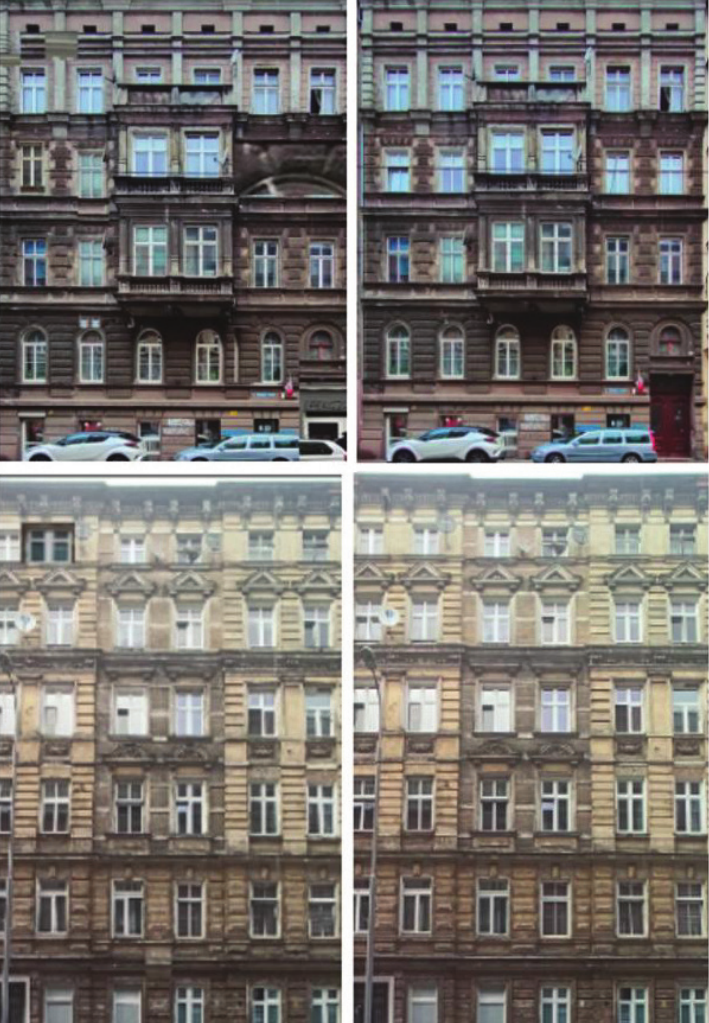
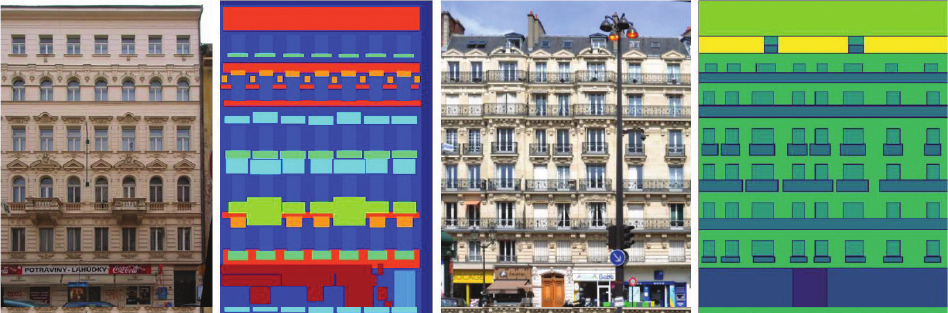
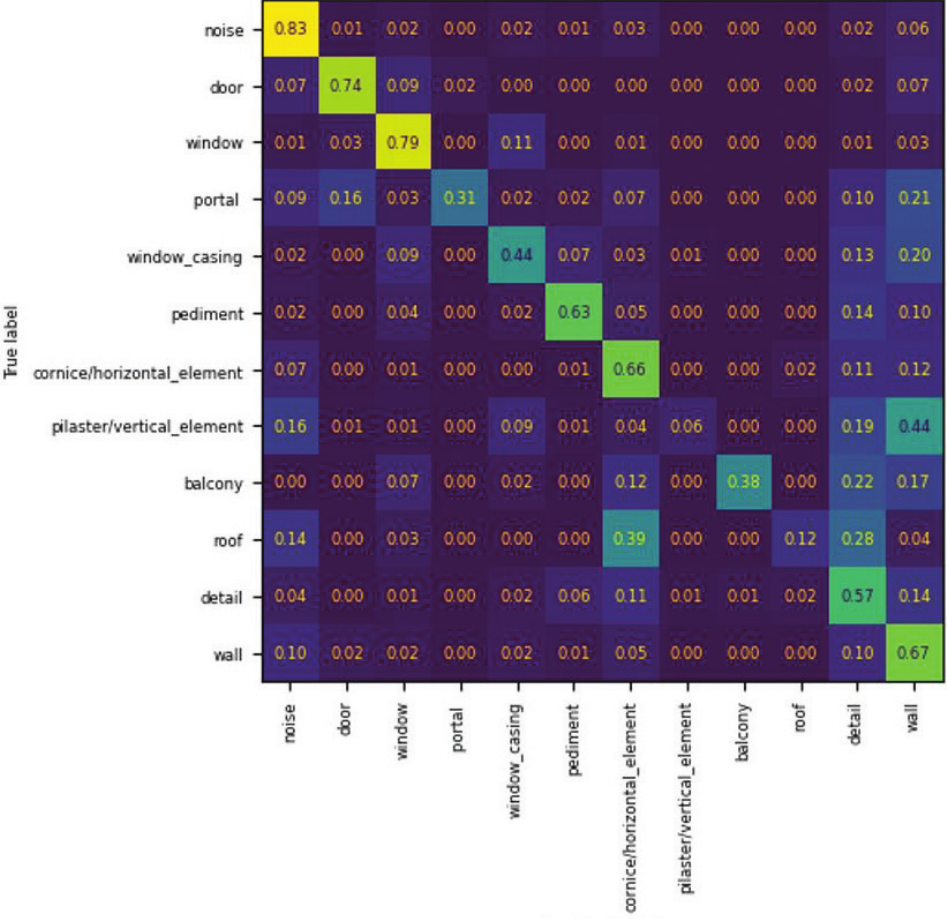
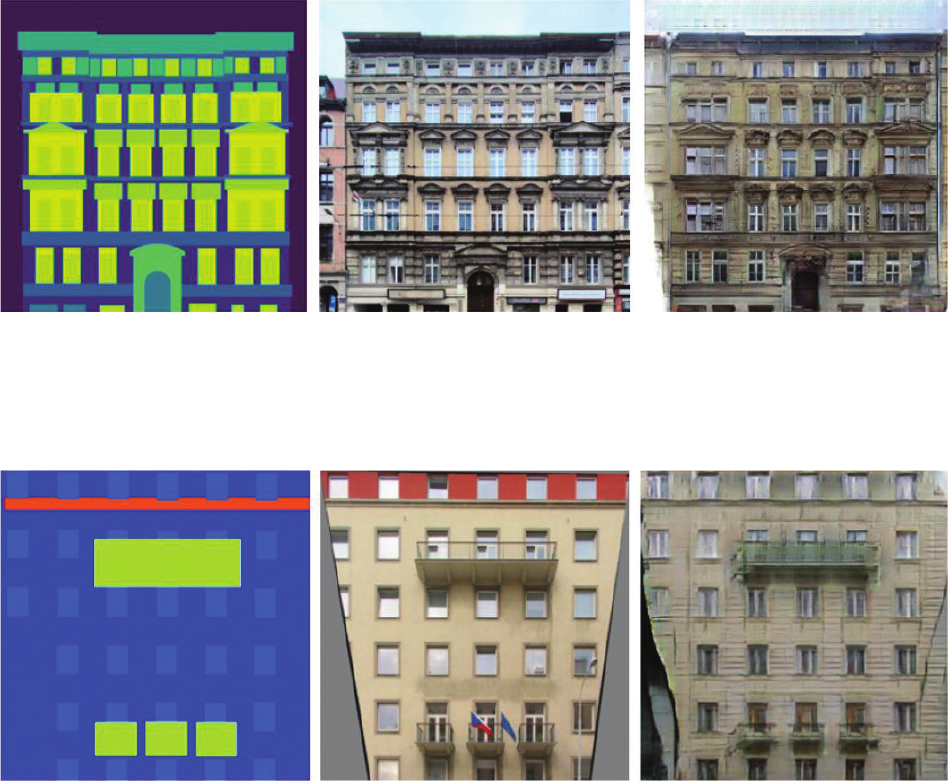
Analysis of the new architectural dataset NeoFaçade and its potential in machine learning 83
oping an architect-friendly generative model capable of
producing highly detailed and contextually accurate archi-
tectural designs.
Future research will focus on leveraging the detailed
metadata included in the dataset. This metadata encom-
passes basic elements of façades and distinguishes between
various architectural styles and elements. Such compre-
hensive annotations oer a rich source of information that
can be employed to train more precise and more sophisti-
cated models. These models will be capable of generating
façades that adhere to rigorous architectural and spatial
specications, thereby meeting the high standards required
in professional architectural design.
Moreover, the planned inclusion of tenements from
Berlin and Szczecin will further enhance the dataset’s di-
versity and robustness. This expansion is expected to sig-
nicantly improve the performance of the presented mod-
els, leading to better and more accurate results. The dataset
will provide a more comprehensive foundation for training
advanced machine learning models by incorporating these
additional urban landscapes.
The NeoFaçade dataset stands out as a high-quality re-
source for machine learning applications in architecture.
Its rich and detailed annotations, combined with contin-
uous updates and expansions, position it as a valuable
tool for developing innovative solutions in architectural
design. The ndings of this study highlight the dataset’s
potential to support the creation of advanced, generative
models that align with the precise demands of architec-
tural practice.
References
Bölek, Buse, Osman Tutal, and Hakan Özbaşaran. “A systematic review
on articial intelligence applications in architecture.” Journal of
Design for Resilience in Architecture and Planning 4, no 1 (2023):
91–104. https://doi.org/10.47818/DRArch.2023.v4i1085.
Enjellina, Eleonora Vilgia Putri Beyan, and Anastasya Gisela Cinintya
Rossy. “Review of AI Image Generator: Inuences, challenges, and
future prospects for architectural eld.” Journal of Articial Intelli-
gence in Architecture (JARINA) 2, no. 1 (2023): 53–65. https://doi.
org/10.24002/jarina.v2i1.6662.
Gadde, Raghudeep, Renaud Marlet, and Nikos Paragios. “Learning gram -
mars
for architecture-specic facade parsing.” International Jour-
nal of Computer Vision 117, no. 3 (2016): 290–316. https://doi.
org/10.1007/s11263-016-0887-4.
Gui, Yingbin, Biao Zhou, Xiongyao Xie, Wensheng Li, and Xifang Zhou.
“GAN-Based Method for generative design of visual comfort in un-
derground space.” IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmen-
tal Science 861, no. 7 (2021): 072015. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-
1315/861/7/072015.
Isola, Phillip, Jun-Yan Zhu, Tinghui Zhou, and Alexei A. Efros. “Image-
to-Image Translation with conditional adversarial networks.” 2017
IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR),
(2017): 5967–76. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.632.
Li, Chengyuan, Tianyu Zhang, Xusheng Du, Ye Zhang, and Haoran Xie.
“Generative AI models for dierent steps in architectural design:
A literature review.” Frontiers of Architectural Research (2024).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foar.2024.10.001.
Liang, Ci-Jyun, Thai-Hoa Le, Youngjib Ham, Bharadwaj R.K. Mantha,
Marvin H. Cheng, and Jacob J. Lin. “Ethics of articial intelligence
and robotics in the architecture, engineering, and construction in-
dustry.” Automation in Construction 162 (June 2024): 105369.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2024.105369.
Marcinów, Aleksandra, Małgorzata Biegańska, Bianka Kowalska, Hu-
bert Baran, Daniil Hardzetski, and Halina Kwaśnicka. “Building
a dataset of Wrocław’s historic tenements: Image annotation for ma-
chine learning applications.” Architectus 79, no. 3 (2024): 55–64.
https://doi.org/10.37190/arc240306.
Martinovic, Andelo, and Luc Van Gool. “Bayesian grammar learning
for inverse procedural modeling.” 2013 IEEE Conference on Com-
puter Vision and Pattern Recognition (2013a): 201–8. https://doi.
org/10.1109/CVPR.2013.33.
Martinovic, Andelo, and Luc Van Gool. “Early Parsing for 2D Stochastic
Context Free Grammars.” Technical Report KUL/ESAT/PSI/1301,
KU Leuven, 2013b.
Nabizadeh Rafsanjani, Hamed, and Amir Hossein Nabizadeh. “Towards
human-centered articial intelligence (AI) in architecture, engineer-
ing, and construction (AEC) industry.” Computers in Human Be-
havior Reports 11 (August 2023): 100319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.
chbr.2023.100319.
Newton, David. “Generative deep learning in architectural design.”
Tech nology|Architecture + Design 3, no. 2 (2019): 176–89. https://
doi.org/10.1080/24751448.2019.1640536.
Pizarro, Pablo N., Leonardo M. Massone, Fabián R. Rojas, and Rafael
O. Ruiz. “Use of convolutional networks in the conceptual structural
design of shear wall buildings layout.” Engineering Structures 239
(2021): 112311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2021.112311.
Peng, Jizong, Guillermo Estrada, Marco Pedersoli, and Christian Des-
rosiers. “Deep co-training for semi-supervised image segmenta-
tion.” Pattern Recognition 107 (November 2020): 107269. https://
doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107269.
Ploennigs, Joern, and Markus Berger. “AI art in architecture.” AI in
Civil Engineering 2, 8 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43503-023-
00018-y.
Rhee, Jinmo, and Jae-Won Chung. “Applicability of Articial Intelligence
in Apartment Complex Design.” In Annual Conference in Architec-
tural Institute of Korea, 2019.
Riemenschneider, Hayko, Urlich Krispel, Wolfgang Thaller, Michael Do-
noser, Sven Havemann, Dieter Fellner, and Horst Bischof. “Irre gu-
lar lattices for complex shape grammar facade parsing.” 2012 IEEE
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2012):
1640–47. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2012.6247857.
Sourek, Michal. “AI in architecture and engineering from misconcep tions
to game-changing prospects.” Architectural Intelligence 3, 4 (2024).
https://doi.org/10.1007/s44223-023-00046-9.
Tyleček, Radim, and Radim Šára. “Spatial pattern templates for recog-
nition of objects with regular structure.” In Pattern Recognition.
GCPR 2013. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, edited by Joachim
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the NCN Miniatura 7 Grant, number 2023/
07/X/ST8/01424.
We would like to express our gratitude to all those who have contribu-
ted to this project: scholars from the chair of the History of Architecture,
Art and Technology of the Faculty of Architecture of Wrocław University
of Science and Technology (Aleksandra Brzozowska-Jawornicka, PhD
Arch, Bartłomiej Ćmielewski, PhD, Maria Legut-Pintal, PhD and Ro-
land Mruczek, PhD) and the students of the Faculty of Architecture, who
took the photographs of the tenements and carried out the annotation
(with particular thanks to Katarzyna Blicharz and Agnieszka Pałka).